What Is a VPN & What Does It Do?
"VPN" stands for "Virtual Private Network," which gives you an accurate but somewhat broad definition of today's commercial VPNs. That's because today's VPNs help you bypass censorship, unblock sites, reach new digital services, download torrents, bypass ISP censorship, and optimize your online gameplay experience. Yes, all that is possible using a single VPN application.
That said, VPNs aren't exactly a new thing. VPN history started in 1996 when a Microsoft employee (Gurdeep Singh-Pall) began his work on PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol). The official specification of that protocol was published in 1999, while the first commercial VPN services started appearing in 2005.
During the last 15+ years, the global VPN industry became a $30 billion industry, expected to reach a market size value of $92 billion by 2027. There are already hundreds of VPN services from all kinds of cyber-sec companies. And, of course, there are some VPN scams as well, as could be expected from such a high-value industry. So, entering today's world of VPNs requires a certain level of caution.
That said, we'll use this guide to explain what a VPN is, how it works, what different VPN features do, what kind of data VPNs hide, whether they're legal to use, how to choose one, and more.
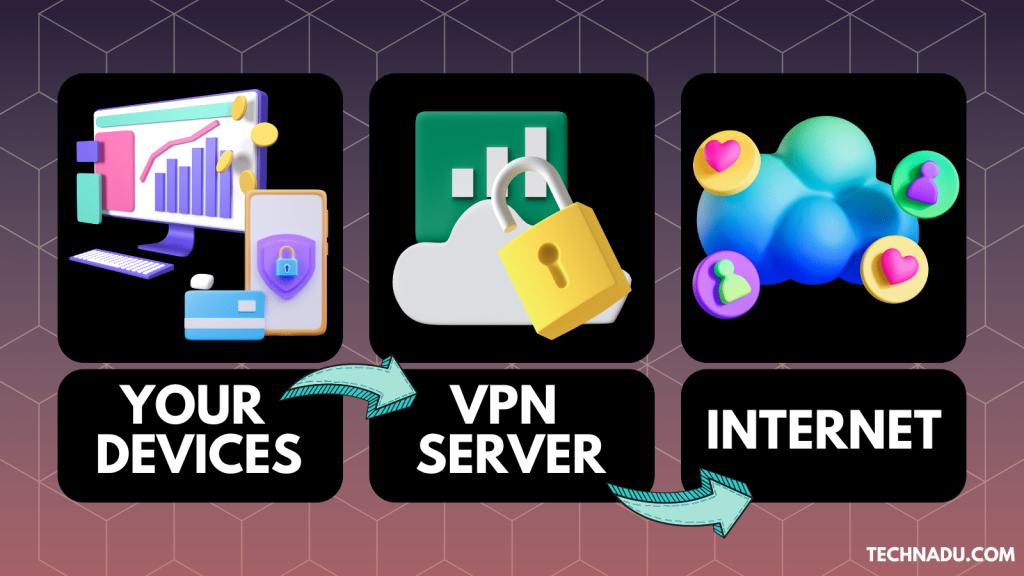
What Is a VPN?
A VPN is a digital service that reroutes and encrypts your Internet data. Once you connect to a VPN server, your incoming and outgoing Internet data becomes invisible to others. By default, every VPN connection is:
- Virtual, as no physical cables are required, meaning that VPNs exist as software on your device.
- Private because no one will see what you do online due to data encryption.
- Networked, as your data will flow from your device through a remote server to the endpoint.
Speaking of the need to create secure connections, you might not even be aware that you emit a lot of information that malicious actors would love to exploit. Some of it is obvious - such as your credit card number, passport details, bank account logins, etc. That’s why finance-related sites and online services that send and receive sensitive information have special technologies to protect that information.
That's great for your bank-specific data, but there’s still a lot of information you broadcast on the Web. It’s not just criminals, either. You also must consider privacy-intruding corporations and governments participating in the 5/9/14-Eyes Alliance.
This is where VPNs come into play. Designed to encrypt your connection, hide your online whereabouts, and ensure no one knows what you do online, VPNs have become the ultimate tool for protecting your privacy. Plus, they're cross-platform, meaning you can use your VPN on an iPhone or Android device, as well as on your computer, streaming device, and even a router.
How Does a VPN Work?
A VPN works by authenticating, encapsulating, and encrypting your Web data. In other words, VPNs process your incoming and outgoing Web data by routing it through secure servers. While doing so, your data becomes unreadable to anyone else online.
Sounds complicated? Let's explain how a VPN works by checking every individual step:
- Step 1 - Authentication: The easiest one to understand is authentication because we all deal with it every day. You have to prove to the VPN that you are really who you say you are. One way VPNs do this is through a plain old username and password.
- Step 2 - Encapsulation: This is the key to how VPNs hide what sort of data you’re sending. They wrap your data packets in their VPN-specific packets through a NAT firewall. So, anyone inspecting those packets will see the same VPN-branded data no matter what’s in there. That's how your Internet provider will know that you use a VPN, but it won't see what you do online.
- Step 3 - Tunneling: Based on your desired VPN location, your data will start flowing through a "tunnel" connecting your device and the chosen server. In most cases, those are physical servers located where they say they're located, but there are also virtual VPN locations.
- Step 4 - Encryption: Encryption is the last piece of the VPN puzzle. This is how the VPN scrambles your data so that even if someone analyzes your packets, it won’t make any sense of that data. Without a special key to unscramble the information, it’s all just gibberish, and only you and the VPN have copies of the encryption keys. There are also VPNs, called double VPNs, which encrypt your data twice by routing it through two servers for those who need extra privacy.
- Step 5 - Decryption: Once your data reaches the server, it gets decrypted by removing the outer packet before reaching its final destination, which can be the server of a website you're trying to open in your browser, for example. That's how others will see the location of your chosen VPN server and not the actual physical location of your device.
What Types of VPNs Exist?
There are four main types of VPN connections: personal VPNs, remote access VPNs, site-to-site VPNs, and SSL VPN connections. While some are suitable for personal use, others are used to connect remote employees to a company's internal network.
Let's first compare the 4 main types of VPNs, and we'll then briefly explain what to expect from each:
- Personal VPN: Most commercial VPN services are personal VPNs, allowing you to connect to their closed networks. While doing so, you get to encrypt your data, make it invisible online, bypass geo-blocks, go around your ISP's throttling, and more. In this case, you can use a VPN with a specific browser through an extension or, even better, a native VPN application.
- Remote Access VPN: If you ever needed to connect to an office network using special software, you used a remote access VPN. These connections secure your access to a company network, making it easier for remote workers to access data and resources easily.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Large corporations typically have a number of offices across a country or multiple countries. They use site-to-site VPN connections to connect all their offices and create a secure and closed network for all their employees simultaneously.
- SSL VPN: Online-based applications, such as file-sharing services and internal directories, typically use SSL VPN connections to secure access. These connections happen automatically in your Web browser as you visit individual websites that require data encryption.
Understanding the Basics of VPN Connections
In this segment, we'll introduce you to terms such as VPN tunnels, VPN servers, IP addresses, and data encryption. To understand how VPNs work and to understand the offerings of today's commercial VPN services, it's important to understand those terms. So, let's explain:
- VPN Tunnel: As its name implies, a VPN tunnel is a connection between your device (computer, phone, streaming device, router, etc.) and your chosen VPN server. That's where encapsulation and encryption happen, meaning that VPN tunnels are private by their nature.
- VPN Server: Commercial VPN services use servers to route your data. Those are standard internet servers configured with special software. As such, their role is to change your IP address and route your traffic before it reaches the Internet, keeping it protected from snoopers.
- IP Address: As soon as you connect to the Internet, your device receives an IP address, which can reveal your location, information about your Internet provider, and more. A VPN assigns you a new IP, preventing websites from seeing your actual information.
- Encryption: As explained earlier, VPN encryption is the process of encoding and securing your data. Today's VPNs typically employ AES-256 or ChaCha20 encryption types, depending on which VPN protocol you use, which makes your data impossible to read even if it gets in the wrong hands.
Understanding the Basic VPN Features
When browsing different VPNs' offerings, you'll encounter different features designed to protect your digital privacy. That said, we'll introduce you to the basic VPN features such as split tunneling, a kill switch, and similar, helping you understand the basics of any capable VPN service.
- Kill Switch: The purpose of a kill switch is to prevent your data from using a non-VPN tunnel when something unexpected happens. For example, if your VPN connection drops by accident, a kill switch will shut down your Web connectivity until you re-connect to your VPN.
- Split Tunneling: Some VPNs allow you to create two data tunnels. Through split tunneling, you can set up a VPN tunnel for applications whose traffic must be routed through a secure server. In the background, you can have a non-VPN tunnel for your regular traffic.
- Obfuscation: Unfortunately, some countries are known for aggressive censorship and blocking access to news sites, social media, and similar. In this case, VPN obfuscation helps with bypassing strong Internet blocks using smaller data packets than usual.
- Zero-Logs Policy: If a VPN features a zero-logs policy, it promises not to collect any of your Web traffic. VPNs are used for privacy, so there's no reason to allow your provider to see what you do online or collect anything other than what's absolutely needed for the VPN to run.
- VPN Leaks: Not every VPN is the same when it comes to privacy protection, so we highly recommend picking one with a reputation for not leaking data. The most common VPN leaks are IP, DNS, and WebRTC leaks, and they're all easy to test for and identify.
What Does a VPN Do?
A VPN can do many things, such as - protect your privacy, secure any Wi-Fi connection, help you work remotely, fight against censorship, and unblock websites. Here's more information:
- Digital Privacy Protection: By encrypting your Internet traffic, VPNs hide your IP address, location-related information, as well as your Web browsing and online activity. In other words, changing your VPN location ensures your privacy is protected on the Web.
- Unblocking Websites & Bypassing Geo-Blocks: Among the many reasons to use a VPN, a prominent one is the ability of VPNs to unblock websites. A VPN will do the trick if you want to access geo-restricted streaming services or any website that doesn't work in your country.
- Fighting Against Censorship: Around the world, censorship is rising, with new types of Web roadblocks appearing daily. If you wish to open up your access to the Web, as well as do that anonymously, you won't find a better tool for the job than a VPN.
- Fighting Against ISP and Third-Party Tracking: If your ISP is known for selective throttling, you'll manage to unleash the full speed of your connection, as your ISP won't be able to throttle activities like streaming, gaming, or torrenting. Plus, VPNs work great for stopping cross-site tracking.
- Optimizing Your Gaming Sessions: By lowering your ping and reducing latency, VPNs can help you achieve more streamlined gaming sessions. Furthermore, they allow you to unblock new gaming marketplaces, access bot lobbies, and obtain region-specific cosmetics.
- Securing (Public) Wi-Fi Connections: There are many reasons why you should use a VPN at home. However, there are even more reasons to use it on the go. VPNs can make any Wi-Fi network secure and private, even open/public Wi-Fi. So, you won't be targeted by Wi-Fi hotspots designed to collect personal data.
- Working Remotely: If you switched to working remotely, you now have to think about the privacy of your sensitive information. A VPN can help establish a data tunnel during work hours, ensuring your work files don't leak on the Web.
What Does a VPN Hide?
A capable VPN can hide all your outgoing and incoming web traffic. That can include your IP address, location, browsing activity, the files you download, and more. Equally important to understanding what a VPN hides is that supplying sensitive information online will be out of your VPN's tunnel.
Let's take a quick look at the most common types of data exposed online and whether a VPN app can help you hide those:
What a VPN Does Not Do?
When it comes to things VPNs can't do, that includes - protecting you from malware, keeping you 100% anonymous online, and stopping cookies from identifying you. Here's more info:
- Anti-Malware Protection: Some VPNs have light malware tools that can scan small files. Also, some offer dedicated anti-malware applications typically available on Windows only. That said, VPNs can't stop malware from reaching your device, especially stronger malware breeds.
- Being 100% Anonymous Online: VPNs hide your online data, which means even your ISP won't see what you do online. However, you must still log in to services like Gmail, Facebook, X, and similar. By logging in, you accept those services to track you - until you decide to log out.
- Digital Tracking via Cookies: Individual websites use cookies for different purposes, like location-based services and personalization. VPNs can't stop those cookies, as that would prevent those websites from working. Also, VPNs don't work against parental controls, in most cases.
Is It Legal to Use a VPN?
Yes, VPNs are legal and safe to use - in most countries. More precisely, there's a small group of countries that have either banned or regulated the use of VPN services. In the rest of the world, it's legal to pick and utilize any commercially available VPN service.
If you check our list of the countries where VPNs are banned, you'll see that totalitarian and authoritarian regimes impose online censorship. However, country-based VPN blocks are practically impossible to implement, so VPNs are used even there - with a great deal of caution, of course.
That said, keep in mind that every country has different digital privacy and data logging laws, so it pays to consider which country to connect to via a VPN. For example, Iceland is great for digital privacy, Canada usually has the fastest servers, while the US helps you unblock most streaming services. You can even obtain GDPR protection outside the EU using a server in a suitable jurisdiction.
How Secure Is a VPN?
VPNs are incredibly secure, especially those that feature robust protocols and encryption. In fact, most of today's commercial VPN services employ such powerful encryption that it would take many years for a powerful computer to decrypt your data.
Of course, every VPN is different, so you need to pay attention to what makes a VPN secure. We highly recommend going for one with solid protocols, an audited no-logs policy, a favorable jurisdiction, RAM-only servers, DNS leak protection, and two-factor authentication.
When using a VPN, remember that you'll have to avoid some threats to your VPN security. For example, you can utilize content blocks to minimize cookies, go for a more secure browser to avoid fingerprinting, opt for using Onion over VPN, as well as pay attention to which digital services you're logged in.
Does a VPN Make You Fully Anonymous Online?
No, a VPN doesn't make you fully anonymous online. The truth is that it's impossible to be completely anonymous on the Web, even when using your browser's Incognito mode.
After all, to use most digital services, you must sign up for an account, register your personal data purposefully, and accept a third-party's website cookies. That is how, for example, Google knows your location even with a VPN active in the background.
That said, a VPN plays a significant role in creating a shield that safeguards your privacy on the Web. As explained in this article, VPNs are the most powerful option to achieve online privacy, even when compared to similar technologies like SSH or VPS, as they offer a user-friendly way to encrypt data, prevent digital tracking, and lower the traces of your online presence.
Who Needs a VPN and Why?
Today's VPN services have numerous practical uses. For example, they're used to bypass geo-blocks, reach new digital services, secure business communications, optimize online gameplay, and more. Let's take a closer look at why needs a VPN and why:
- General (Home) Users: VPNs are helpful for everyday digital privacy protection as you browse the Web, download data, and more. They make sure you're not tracked online, targeted by ads, and targeted by malicious actors when using public Wi-Fi connections. Furthermore, they help you avoid price discrimination and even get around ISP throttling.
- Streaming Enthusiasts: One of the biggest reasons for VPNs' popularity is their ability to unblock streaming services available in certain countries only. To make that happen, you only need to connect to a server in another country. If you're in the US, you can also bypass blackout restrictions imposed by sports-streaming services.
- Torrenting Enthusiasts: A VPN that is friendly towards P2P helps you access blocked torrent sites and can anonymize your downloads/uploads. If your Internet provider is working actively against P2P-related activities, and if you fear getting a copyright infringement notice, all you need is a speedy VPN that imposes no P2P restrictions.
- Gaming Enthusiasts: By re-routing your traffic more efficiently, VPNs help reduce ping, which leads to more responsive gaming sessions. Other benefits of gaming over a VPN include getting to play geo-restricted games, avoiding account/IP bans, accessing more gaming stores, unlocking special cosmetics and bonuses available in certain countries only, and more.
- Travelers: You'll often encounter blocks and access restrictions when traveling outside your home country. For example, access to your bank account might be flagged, as you'll use a foreign IP address. To avoid VPN blocks and ensure access to their often-used services, travelers often employ VPNs with a sizable server network and strong content-unblocking abilities.
- Journalists and Activists: Those in need of a secure communication channel often rely on individual messaging apps to reach their contacts. Going that route is perfectly fine, but employing a VPN also helps journalists and activists encrypt their digital traffic, use a wider variety of messaging apps, access the Dark Web more securely, and hide their physical location.
- Businesses: Both small and large businesses use VPNs to encrypt important data, allow remote workers to access internal resources securely, and protect against digital threats. While smaller companies can use commercial VPN services, large corporations typically stick to custom enterprise VPN solutions.
What to Look for When Choosing a VPN?
The most critical features when looking for the best VPN are data encryption, split tunneling, kill switch, data leak protection, and simultaneous connections. Here's more info:
- Data Encryption: All VPNs use data encryption. They use several VPN protocols to dictate how rigorously your data is encrypted. If you want the best security, pick OpenVPN. You can go with WireGuard if you need fast performance.
- Overall Speed and Performance: Every VPN performs differently, which is why speed tests are an important segment of the way we review VPNs. We recommend picking a VPN with a sizable network and optimized servers for specific online activities.
- Data Logging Policy: There's no reason to allow anyone, and that includes your VPN, to track you online. Many VPNs offer zero-logs policies, which means they won't see your online whereabouts. Just make sure to pick one with an audited no-logs policy.
- Server Network Size and Spread: A sizable server network is needed to unblock websites, obtain specific IP addresses, and ensure that you get stable and fast performance. Luckily, you shouldn't have a hard time finding a VPN with servers across the globe.
- Split Tunneling: This feature allows you to set up two tunnels. For example, you can have one tunnel for your VPN data, ensuring you download torrents anonymously, for example. At the same time, you can keep a regular data tunnel, giving you access to websites that might block VPNs.
- Kill Switch: Your connection to a VPN server can drop at any moment. In that case, your data will leak on the Web, which is essential to prevent when doing sensitive tasks online. You can prevent that from happening using a kill switch.
- Data Leak Protection: As mentioned above, your data can leak when your VPN connection drops. However, less secure VPNs can leak your data even through their VPN tunnels. Plus, they'll force you to deal with CATPCHAs more often. So, it's crucial to pick a VPN with high-end security.
- Simultaneous Connections: VPNs typically limit the number of concurrent connections, which means you can run them on 5 to 10 devices simultaneously. So, make sure to pay attention to this VPN feature before buying a VPN.
- Customer Support: An easy way to spot a fake VPN is to check its customer support. You should aim for a VPN with 24/7 live chat, which adds credibility to that service. Plus, you'll want extensive documentation, FAQs, tutorials, and more.
- Pricing and Money-Back Policy: A high-end VPN doesn't have to cost a lot, especially if you pick a long-term subscription. That said, keep in mind that most VPNs have 30-day money-back policies, giving you plenty of time to test-drive them.
How Much Does a VPN Cost?
Most VPNs come with several subscription plans, allowing you to pay on a monthly or yearly basis, giving you a lot of flexibility in optimizing the cost of a VPN. This way, VPNs can cost from around $10.00 to around $15.00 per month. However, paying upfront usually brings steep discounts of more than 50%.
If you break down their yearly prices into monthly payments, you'll need to pay from around $2.50 to around $8.00. Of course, by choosing a yearly plan, you must pay for the whole year upfront. It's also worth mentioning that you can find some pretty great deals occasionally, so it's worth keeping your eye on periodic promotions.
Paid VPN vs. Free VPN vs. Free VPN Trial
When it comes to the price of VPNs, you can choose from free and premium VPNs. However, many premium VPNs also offer free VPN trials, which is an excellent way to test those services without any financial risk.
However, those terms can be a bit confusing, so let's help you compare premium VPNs, free VPNs, and free-trial VPNs. Here's a table that explains the most prominent differences:
As you can see, it's hard to recommend free VPN services. That's because most free VPNs are not safe, as they're mainly designed to exploit your privacy. On top of that, they come with strict data allowances, and they're usually painfully slow.
That said, we recommend going for a free VPN trial if you're unsure about spending money on a VPN service. By going for a free trial, you can test your chosen VPN with no limitations. If you change your mind, you'll have your money back - as simple as that. And if you already know what to expect, make your options broader and go for a premium VPN from the get-go.
How to Set Up and Use a VPN
VPNs are available for just about any device or platform, and there are software and hardware VPNs. That said, check out the following guides produced by our team on how to set up a VPN on any device:
Of course, setting up a VPN is only one part of the process. You'll also want to know how to check if your VPN is working, which also helps you check for possible data leaks. Furthermore, it's also worth knowing how to check if you have a VPN installed, as having multiple applications of this type on your system can cause a software conflict, so you'll want to avoid using multiple VPNs, which is fixed by removing a VPN.
We'll also add that it's safe to turn off a VPN once you're done using it - but practically all premium VPNs offer unlimited bandwidth. So, there's no reason to fear keeping your VPN connection alive at all times.
How Do I Troubleshoot a VPN?
The best way to troubleshoot a VPN is by connecting to a different VPN server, switching to another VPN protocol, as well as by reinstalling/updating your VPN software. Also, don't forget that you can always count on your VPN's support team, which is why we're recommending picking one that offers 24/7 live chat support.
You'll be happy to know that resolving VPN issues is typically straightforward. You'll find 20+ actionable tips in our central VPN troubleshooting guide, which should be your go-to resource in case of any troubles. The same applies to VPN error code fixes, which usually require very specific steps, based on the type of error code that appears on your screen.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a VPN?
There are numerous pros and cons to using a VPN. Of course, the pros outweigh the cons, as VPNs have become highly streamlined tools that don't affect your device's performance or web browsing habits. Instead, they work in the background without much input from you.
So, let's take a brief look at some of the most prominent ones.
- Content Unblocking: VPNs provide a way to see content that governments don’t want their citizens to see. So, if you live in a country that censors the Internet, such as China for example, a VPN could open your eyes to a world of new opinions, especially if you combine Tor with a VPN.
- Making Public Wi-Fi Safe: You can set up a VPN on any device to ensure that no matter which shady venue’s Web connection you use, it’s as safe as your own home Wi-Fi.
- Speeding Up Your Web Connection: Because of the way VPNs work, your ISP won't see your Web browsing data since it’s all hidden inside your VPN tunnel. That means you get all the speed your connection can provide, minus a little VPN overhead, of course.
- Securing Your Mobile Internet: As soon as you leave the comfort of your home Wi-Fi hotspot, you’re probably switching to your mobile data provider. If you don’t have a VPN on your phone, you’ll start leaking private data through your mobile provider the second you’re out of your home Wi-Fi range.
VPNs are beneficial in a huge number of ways - but they also come with some disadvantages. Here's more information about that side of VPN services:
- They Aren't All-In-One Security Solutions: As explained earlier, VPNs won't protect you against malware. They're also not a replacement for dedicated firewall apps. As such, they don't handle every possible aspect of your cyber-security.
- You Can't Unblock Every Single Website: Today's VPNs are hugely powerful in terms of unblocking websites. However, so are the efforts of websites to prevent VPNs. Luckily for you, there's plenty you can do to bypass firewall blocks.
- Unthrottled Connections Will Slow Down: If your Internet connection isn't throttled by your ISP, a VPN will slow you down. A capable VPN service will make your connection slower by 10-20%, on average.
Final Thoughts - Is a VPN Worth It?
Yes, definitely - VPNs are worth it! As explained throughout this guide, getting a VPN means you'll be taking care of your digital privacy, which has become imperative in this day and age.
However, keep in mind that not all VPNs are worth it. In fact, it's better not to use a VPN than to use a free or an unknown one. Since they handle your data, they can also take advantage of your data. So, make sure to pick a trustworthy one, with a long history of serving its users.
As long as you pick a trustworthy and reputable VPN, you can rest assured that your privacy is protected on the Web. So, no matter if you want to keep trackers at bay, unblock sites, download torrents, or play online games - getting a VPN is the best choice you can make right now.
Just remember that it's imperative to go for a reputable VPN brand. Trying to save money by picking a free VPN or an unknown one can harm your privacy. So, if you decide to use a VPN, remember that spending a few more dollars per month can really go a long way.
We hope you liked our comprehensive guide on explaining the basics of VPNs. If you have any questions for us, make sure to post them just below. Thanks for reading!