WebRAT Malware Campaign Targets Researchers via GitHub Repositories Containing Fake PoC Exploits for Legitimate Vulnerabilities
- Deceptive distribution: The WebRAT malware is being distributed through GitHub repositories disguised as PoC exploits for high-severity flaws.
- Targeted audience: Focus shifted from gamers to inexperienced cybersecurity professionals, students, and researchers looking for vulnerability information.
- Malicious payload: The malware acts as a backdoor, stealing credentials and performing spyware functions like keylogging and screen recording.
A malicious campaign is leveraging GitHub to distribute the WebRAT malware, a capable backdoor Trojan. Threat actors are creating repositories containing fake Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploits for legitimate high-profile vulnerabilities. These repositories are designed to attract novice cybersecurity professionals and students searching for code related to newly disclosed security flaws.
GitHub Repositories Used as a Lure for Malware
To appear credible, the repository descriptions include detailed, structured information about the vulnerabilities, likely generated by AI to mimic authentic vulnerability reports, specifically:
- CVE-2025-59295 (8.8)
- CVE-2025-10294 (9.8)
- CVE-2025-59230 (7.8)
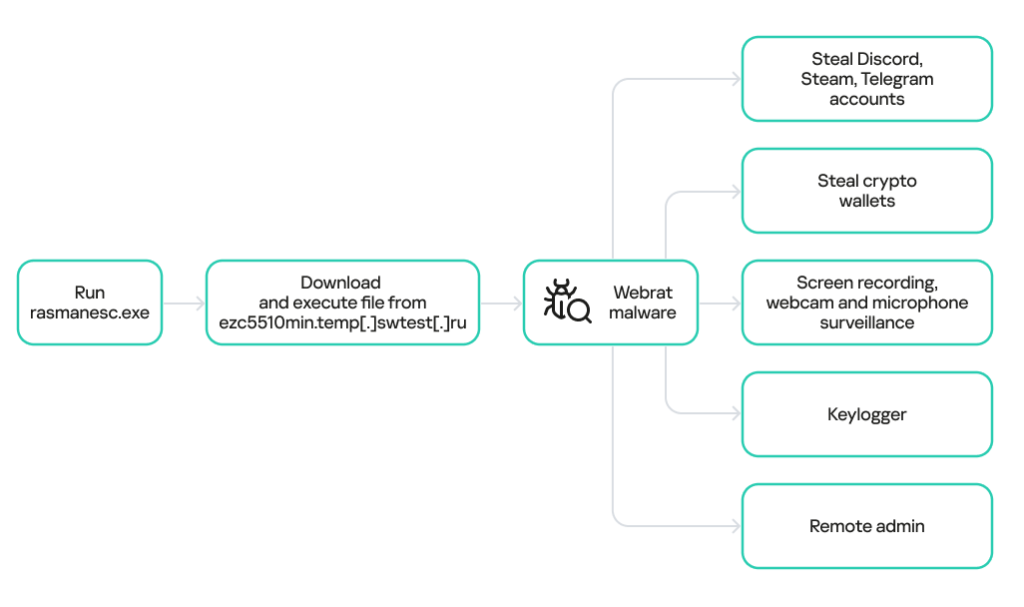
The infection chain begins when a victim downloads a password-protected archive from the malicious repository, according to the latest SecureList report. Inside the archive is an executable (rasmanesc.exe) that, when run:
- elevates its privileges,
- disables Windows Defender to evade detection,
- downloads and executes the final WebRAT payload from a hardcoded command-and-control (C2) server.
WebRAT is a backdoor that provides attackers with extensive control over an infected system. Its capabilities include:
- stealing data from cryptocurrency wallets, Telegram, Discord, and Steam accounts,
- comprehensive spyware functions such as screen recording, webcam and microphone surveillance, and keylogging.
Shifting Targets
The primary targets of this GitHub malware campaign are now inexperienced security researchers and students who might download and execute the supposed exploit code outside of a secure, isolated environment.
This method represents a significant shift from WebRAT's previous distribution channels, which primarily involved game cheats for popular games like Rust, Counter-Strike, and Roblox, and cracked software.
However, the current WebRAT version is no different from previous ones, which are well documented. This new focus on security professionals highlights an increasing trend of malware targeting researchers.
WebRAT Mitigation
Professionals are strongly advised to analyze any code from unverified sources, especially GitHub, within a sandboxed or virtualized environment.
It is critical to never run unknown exploits on production systems or personal devices containing sensitive information. Maintaining up-to-date security solutions and exercising caution with open-source code are essential defense measures.
In October 2024, gamers were targeted with Lua-based malware disguised as cheating script engines. Earlier this year, a GitHub phishing campaign employed a security alert lure to install a malicious OAuth application.