Ivanti EPMM Zero-Day RCE Flaws Actively Exploited, Affecting ‘Very Limited’ Number of Customers
- Zero-Day Discovery: Security researchers have identified two critical RCE flaws in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) that are currently being exploited in the wild.
- Active Exploitation: Attackers execute arbitrary commands on unpatched systems, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive enterprise networks.
- Urgent Patching: Ivanti has released emergency security updates to address these vulnerabilities and urges administrators to apply them immediately.
Two Ivanti EPMM zero-day flaws have been disclosed that allow unauthenticated remote code execution on affected appliances. These vulnerabilities allow unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely, posing a severe threat to organizations utilizing the platform for mobile device management.
This level of access facilitates deep infiltration into corporate networks, enabling data exfiltration, lateral movement, and the deployment of persistent malware.
Mechanics of the Exploitation
Tracked as CVE-2026-1281 and CVE-2026-1340, these code injection flaws enable unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) and affect the In-House Application Distribution and Android File Transfer Configuration features.
Ivanti telemetry indicates that attackers are already incorporating these zero-day vulnerabilities into their attack chains, impacting “a very limited number of customers.”
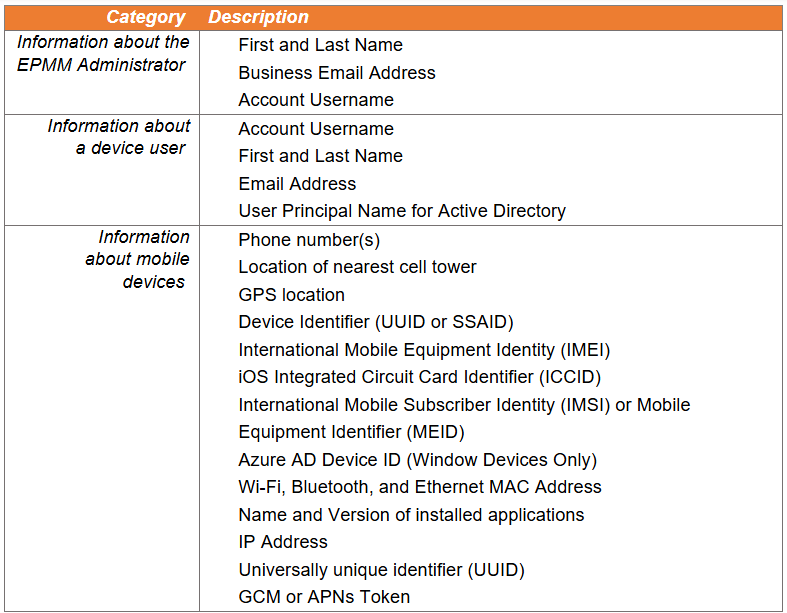
EPMM also contains sensitive information about devices managed by the appliance, including admin and device user names and email addresses, as well as details associated with mobile devices, such as phone numbers, GPS locations, and IP addresses.
Mitigation and Cybersecurity Updates
In response to these critical findings, Ivanti has issued expedited cybersecurity updates to patch the affected versions of EPMM. Security administrators are strongly advised to prioritize deploying these patches immediately.
Customers should apply either RPM 12.x.0.x or RPM 12.x.1.x; they do not need to apply both, as they are version-specific, not vulnerability-specific.
“We strongly encourage all EPMM customers to adopt version 12.8.0.0 once it has been released later in Q1 2026,” the advisory said. This will not require reapplying the RPM script.
Other Ivanti products are not impacted, including cloud products such as Ivanti Neurons for MDM, Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM), and Ivanti cloud products with Sentry.
This month, a critical RCE vulnerability in legacy D-Link DSL router models was signaled. In November, the Cisco and Citrix zero-days CVE-2025-20337 and CVE-2025-5777 were exploited.