When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
What Is VPN Split Tunneling: How it Works and Why You Might Need it in 2026
A split tunneling VPN allows you to exclude a part of your Internet traffic from your VPN connection. This is a useful feature for those who want to stay anonymous on the Web without losing speed in other activities like streaming videos or downloading files.
For example, you may prefer to use a VPN when torrenting. However, VPNs can cause latency issues in online games. By using a split tunneling VPN instead of full tunneling, you can route your gaming traffic outside the VPN and enjoy good latency - while getting to download torrents safely and anonymously.
In this article, we’ll discuss what split tunneling is, how it works, and how you can enable it on your device. We’ll also talk about its different types, pros and cons, and risks, as well as review the best VPNs offering this feature. So, without further ado, let’s dive right into it.
What Is VPN Split Tunneling?
VPN split tunneling is a feature that allows you to route a part of your traffic through an encrypted tunnel while the remaining data goes through an open connection. In other words, it gives you the freedom to secure specific applications and website URLs of your choice.
Imagine this scenario. You want to sign into a geo-restricted service in the US. But at the same time, you want to get local search results on TikTok in India. Using a regular VPN means that you have to sacrifice one activity for the other. With split tunneling, you can simultaneously access the geo-blocked app with a US IP and use TikTok with your actual Indian IP address.
Similarly, split tunneling is useful for remote workers who are using an enterprise-grade VPN because it prevents the unnecessary load from additional traffic and keeps their local activities private.
Generally, a regular VPN connection will reduce your Internet speed because it fully encrypts the traffic. However, a split tunneling VPN secures sensitive data without slowing down other Web activities.
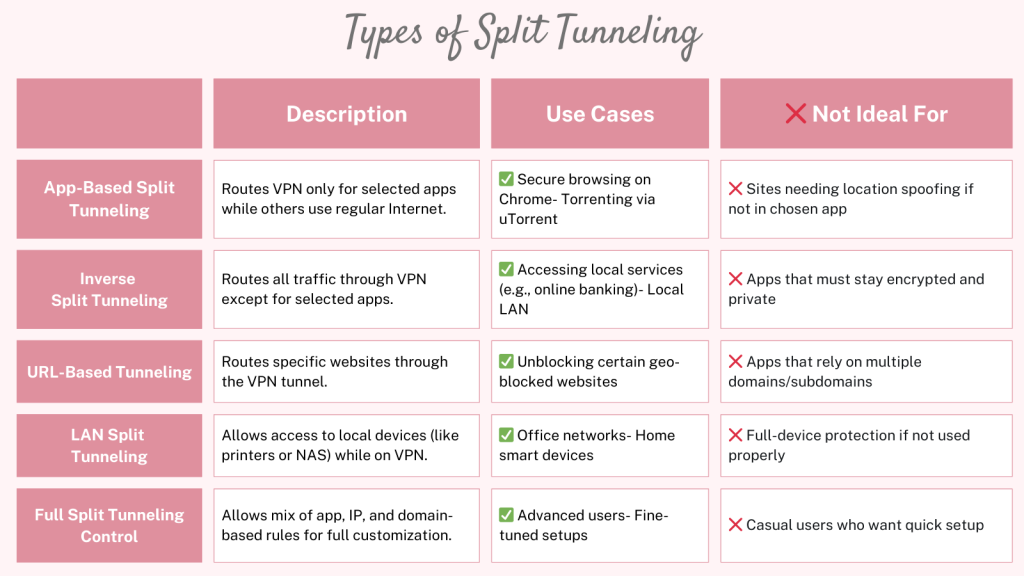
Types of VPN Split Tunneling
There are 5 types of VPN split tunneling: URL-based, app-based, and inverse split tunneling. Let’s take a quick look at each of these.
- URL Split Tunneling: It allows you to encrypt specific URLs via the VPN. Usually, you can find this feature in the browser extensions of VPNs.
- App Split Tunneling: This is similar to URL split tunneling, but it applies to applications instead of URLs. You can encrypt a specific application and let the remaining traffic travel via an open network.
- Inverse Split Tunneling: It automatically routes your whole traffic via the VPN except the applications or URLs that you choose to exclude. In a way, inverse split tunneling works the opposite of the first two types.
- LAN Split Tunneling: It lets you access local network devices (like printers, file servers, or smart home hubs) while connected to a VPN. It’s useful when you're working remotely but still need access to your home or office LAN.
- Full Split Tunneling Control: Some VPNs offer full customization over tunneling. This includes mixing app-based, IP-based, and domain-based rules, giving you complete control over what goes through the VPN and what doesn’t.
How Does VPN Split Tunneling Work?
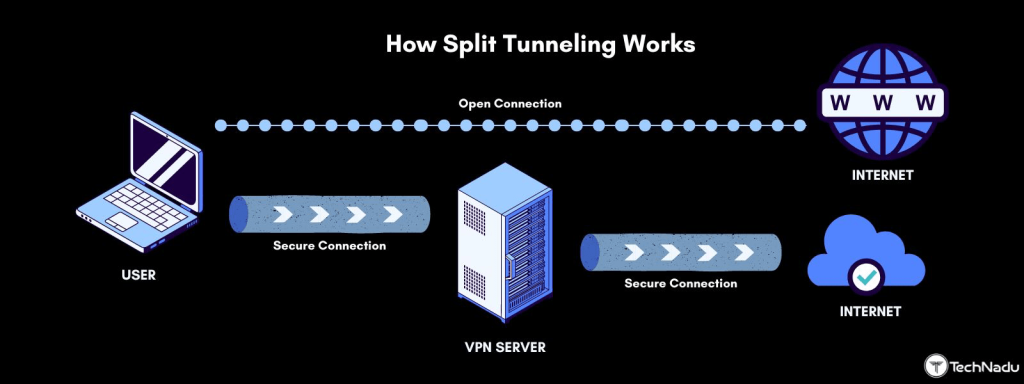
Split tunneling works by splitting your Internet traffic into two parts. The first part is routed through the VPN, while the second part flows through your regular Internet connection.
It will become easier to visualize a split tunneling VPN if you first learn how VPNs work. Simply put, a VPN secures your connection by acting as an intermediary between you and the Internet.
When you turn on a regular VPN, this is what happens:
- VPN app receives your data and encrypts it.
- It sends the data to its secure server.
- The server decrypts this data and sends it to the target website.
Such an open VPN connection will encrypt every last bit of your data. However, it will slow down the Internet speed because your data will have to travel through an extra hoop.
On the other hand, this is what happens when you turn on split tunneling:
- Your Internet traffic gets divided into two parts.
- A VPN encrypts one part of your Internet traffic and sends it to a secure server.
- The secure server decrypts your traffic and sends it to the target website.
- The other part of your traffic goes through the open connection.
The best part is that you can decide which data should go through the open connection and which should pass through the VPN.
Unfortunately, not all VPNs offer split tunneling. So, it’s important to use a capable VPN. We recommend NordVPN due to its advanced split tunneling features.
When to Use Split Tunneling?
You should use split tunneling when you want to secure sensitive data without slowing the overall Internet speed. It is also useful when you’re in a country with strict government censorship or working remotely.
Here’s more information about these use cases.
- To secure data without slowing down other activities: Imagine torrenting and streaming a 4K video on YouTube. You’ll prefer a VPN for torrenting, but for QHD streaming, an open connection is better due to higher speeds. Using split tunneling, you can encrypt the torrenting app and let the video stream continue on the open connection.
- To Access LAN Devices While Using a VPN: Sometimes, when connected to a VPN, you can’t access devices on your local network like printers, file servers, or smart TVs. Split tunneling lets you keep access to these devices by routing only external traffic (e.g., web browsing) through the VPN.
- To Avoid Bandwidth Caps or Data Throttling: Some ISPs throttle VPN traffic. With split tunneling, you can choose to encrypt only the apps that need privacy, while keeping the rest on your normal network—possibly avoiding triggering bandwidth restrictions.
- You live in a country with strict government censorship: If your country has strict censorship laws, like Saudi Arabia and China, you can use a VPN to access censored websites. But you may also want to enjoy the best speeds while watching movies on local streaming services. In this case, you can exclude the streaming apps from the VPN connection using split tunneling.
- To work remotely: If you’re working remotely, you’ll want to encrypt some sensitive work information. At the same time, you may also need access to localized search results and regional content on Web platforms. With a split tunneling VPN, you can get these things done simultaneously.
Of course, split tunneling can have endless use cases. After knowing the basics of split tunneling, you can easily figure out if this feature is useful for you.
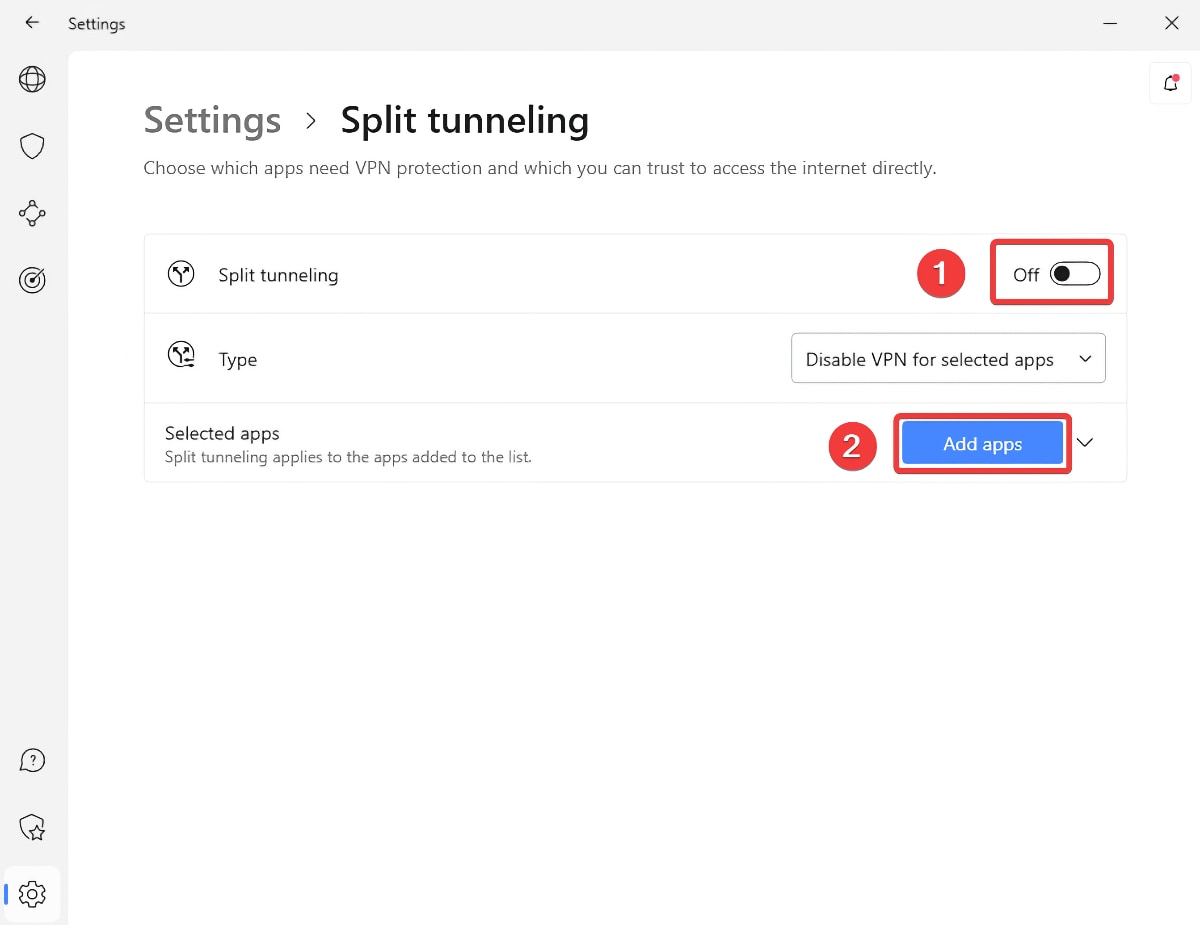
How to Enable Split Tunneling on a VPN?
Once you subscribe to a VPN that supports split tunneling, you need to install its app. Log in, access your VPN's settings, and enable the feature. These are the steps you need to take:
- Sign up for a VPN that supports split tunneling (we recommend NordVPN).
- Download and install your chosen VPN application on your device(s).
- Log in to the VPN by entering your account credentials.
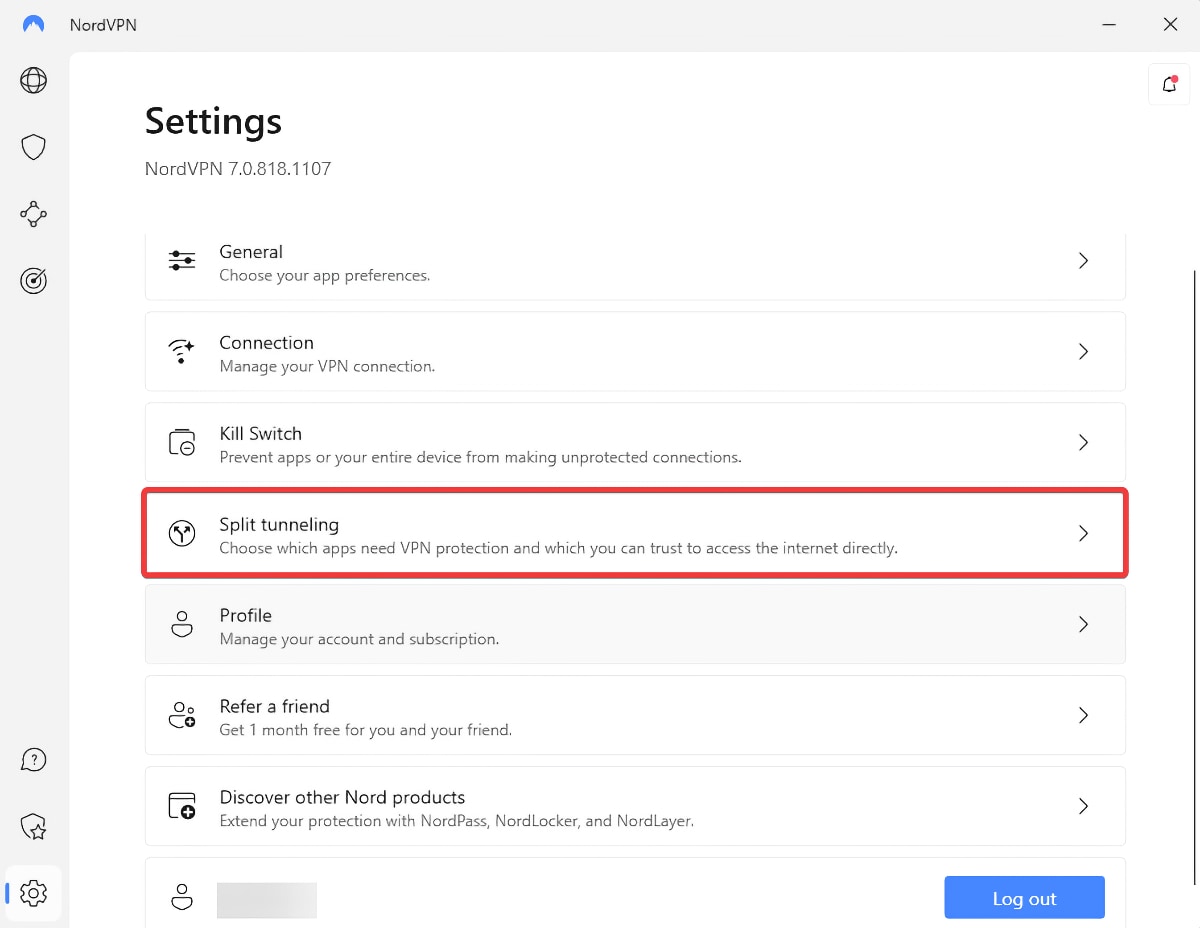
- Visit the application's settings (there should be a gear-like icon in most cases).
- Look for a section that contains split tunneling-related options.
- You'll be asked to enable split tunneling and add specific applications to the list.
- That’s it! Now, you can enjoy strategic, selective browsing via split tunneling!
Be careful when adding applications to your split tunneling list. Keep in mind that some VPNs allow you to add applications that will use your VPN data tunnel, while others might ask you to add applications that will use your regular data tunnel. There should be a clear notification, though.
Pros & Cons of VPN Split Tunneling
Editor's Pick: Best Split Tunnel VPN in 2026?
At TechNadu, we have tested 65+ VPNs, and based on this rich experience, here’s a list of the best VPNs with split tunneling in 2026. However, we do recommend you check out our guide to the best Split Tunneling VPNs in order to analyze why we have chosen them. In that guide, we have made a thorough comparison. We have also mentioned how to turn on the split tunneling feature for each of the VPN we recommend.
Nevertheless, let's have a quick glance at each of them.
- NordVPN: Cut through the noise with precision as its robust split tunneling lets you lock down sensitive apps while keeping everything else lightning-fast.
- Surfshark: Surfshark’s “Bypasser” gives you total traffic control—secure what matters, skip what doesn't, and stream or bank without compromise.
- ExpressVPN: ExpressVPN offers intuitive, per-app split tunneling and even supports inverse tunneling, giving you ultimate flexibility in how your data flows.
- CyberGhost VPN: CyberGhost’s split tunneling on Android and Smart Rules on Windows help you protect sensitive tasks while bypassing restrictions where needed.
- Private Internet Access: PIA’s powerful split tunneling lets you choose exactly which apps use the VPN—ideal for multitasking securely without sacrificing speed.
What Are the Risks of Split Tunneling?
Split tunneling comes with its own set of risks, such as cyber threats, corporate risks, and bypassing security measures. Let’s take a quick look at these risks.
- Not being secure if you fail to set it up properly: Hackers may find a vulnerability and access your information. An improper setup will also reveal all Internet activity to the ISP.
- Risks in corporate environments: IT branches in corporate sectors can lose visibility of what their employees browse during work time. Furthermore, if the employee is using an unsecured network, the security of your corporate system can be at risk.
- Bypass security measures: Split tunneling may sometimes cause you to accidentally ignore proxy servers that keep traffic secure.
Split Tunneling vs Full Tunneling
Simply put, a full tunnel refers to a regular VPN connection that encrypts all your Internet traffic, while split tunneling results in partial encryption of the traffic. Here’s a quick comparison between both types:
That being said, full tunneling is better than a split tunneling VPN because it provides maximum security and privacy.
Final Thoughts
VPN split tunneling is one of the most flexible and practical features a VPN can offer, especially in 2026, when multitasking across secure and regular networks is more common than ever. It gives you the best of both worlds: privacy where you need it and speed where you want it.
Whether you're streaming, torrenting, gaming, or working remotely, split tunneling lets you decide which traffic stays protected and which flows freely. Just remember to set it up correctly to avoid accidental data leaks.
We have tested many VPNs with split tunneling, but NordVPN is our top recommendation because it gives you three options: inverse (all supported platforms), app-based (Windows), or URL-based tunneling. Furthermore, it offers the latest military-grade AES-256-bit encryption and obfuscated servers.
We hope that this article answers your questions about split tunneling VPN. Feel free to leave a comment below if you have any other questions for us. Thanks for reading!