EU Website Exploited to Advertise Scam and Pirate IPTV Platforms
- The official EU statistics portal was hijacked to advertise scam or pirate IPTV platforms.
- Hackers uploaded fraudulent, SEO-optimized PDFs to Eurostat's online platform, which Google indexed as legitimate.
- The attack raised critical questions about website security and the risks of SEO-focused cyberattacks.
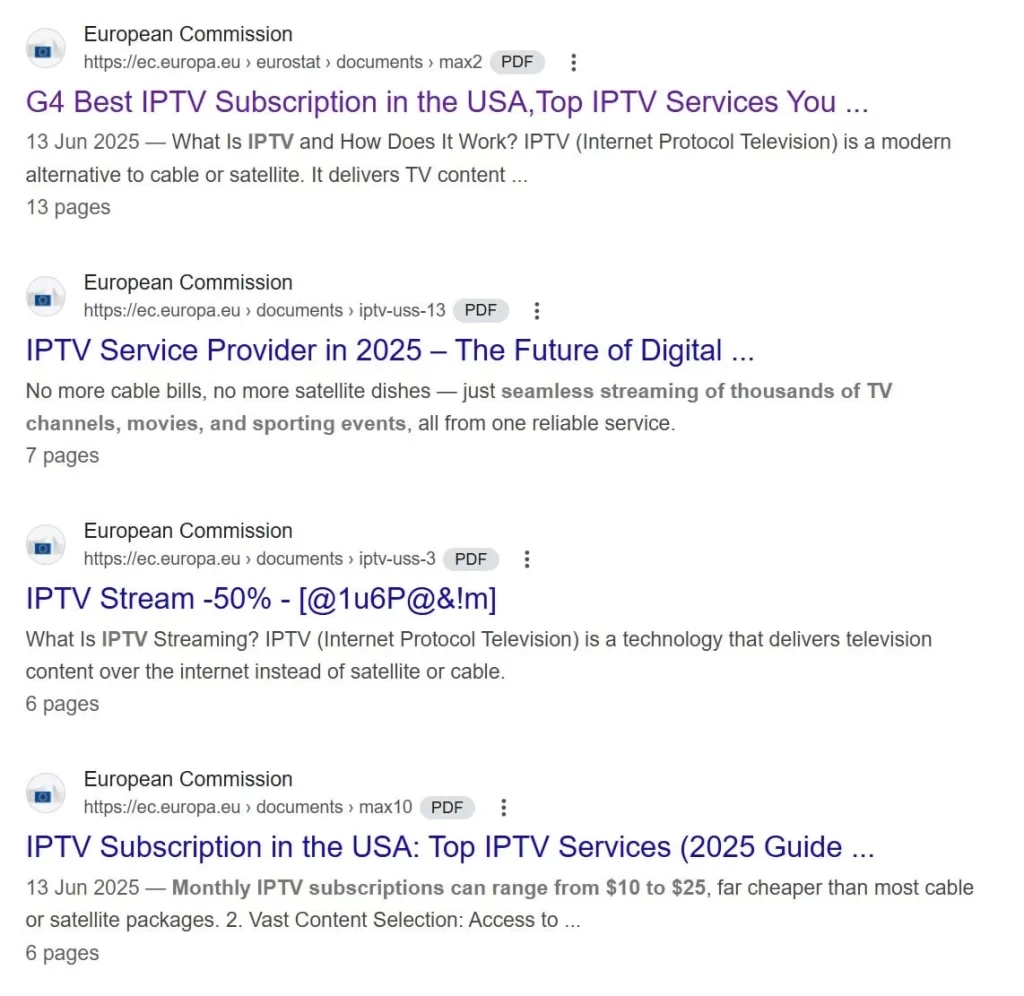
Cybercriminals exploited the European Union's Eurostat website to promote illicit IPTV services. The exploitation centered on the upload of fraudulent PDF documents to Eurostat's online platform.
These files, which masqueraded as legitimate information, contained advertisements for questionable IPTV services.
Promising access to thousands of streaming channels, on-demand content, and premium platforms like Netflix and Disney for a nominal fee, the services were either outright scams or unauthorized operations selling pirated content.
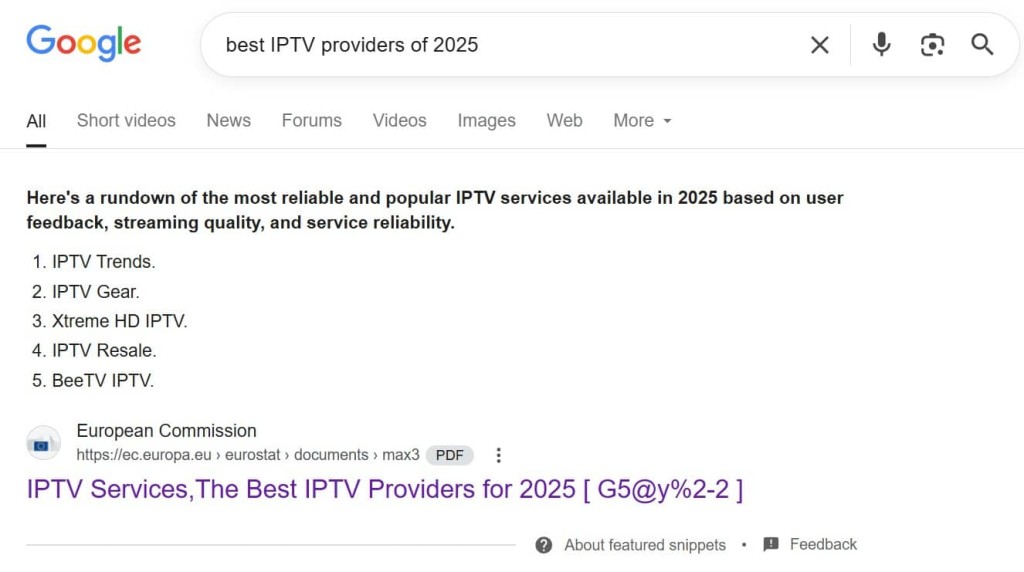
The malicious PDFs were optimized with SEO techniques, ensuring they ranked highly in search results for queries like "best IPTV providers of 2025."
Google’s AI overview even mistook the fraudulent documents as official EU endorsements, thereby compounding the issue and amplifying their visibility, which inadvertently promoted scams and piracy.
This incident underscores critical flaws in platform upload functionalities, which provide entry points for malicious actors to misuse trusted domains for phishing, scams, and illegitimate advertising campaigns.
Additionally, when authoritative sources are hijacked, users are less likely to question the content's legitimacy, increasing the potential impact of these scams.
In February, hackers exploited a Europa.eu subdomain to facilitate fraudulent redirects and achieve high-ranking search results. They manipulated Google’s algorithms using in-demand keywords like “Super Bowl,” paired with phrases like “stream/download/free,” to steal personal information, including credit card details.