Critical Privilege Escalation Flaw Found in Microsoft Active Directory dMSA Feature
- A privilege escalation flaw in the Active Directory dMSA feature allows attackers to manipulate the dMSA migration process.
- The vulnerability affects organizations using Microsoft Windows Server 2025 and stems from inadequate validation.
- Privilege escalation could enable threat actors to compromise any AD principal, including administrator accounts.
A critical elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerability affects organizations using Microsoft Windows Server 2025. The root of the issue lies in delegated Managed Service Accounts (dMSA), a feature introduced to simplify service account management in Active Directory (AD).
Akamai research has uncovered how attackers can manipulate the dMSA migration process to escalate their permissions and compromise any AD principal, including privileged accounts like Domain Admins.
The dMSA accounts are intended to streamline the migration from legacy service accounts by inheriting their permissions. According to security researcher Yuval Gordon’s analysis, the vulnerability emerges due to inadequate validation in the migration process.
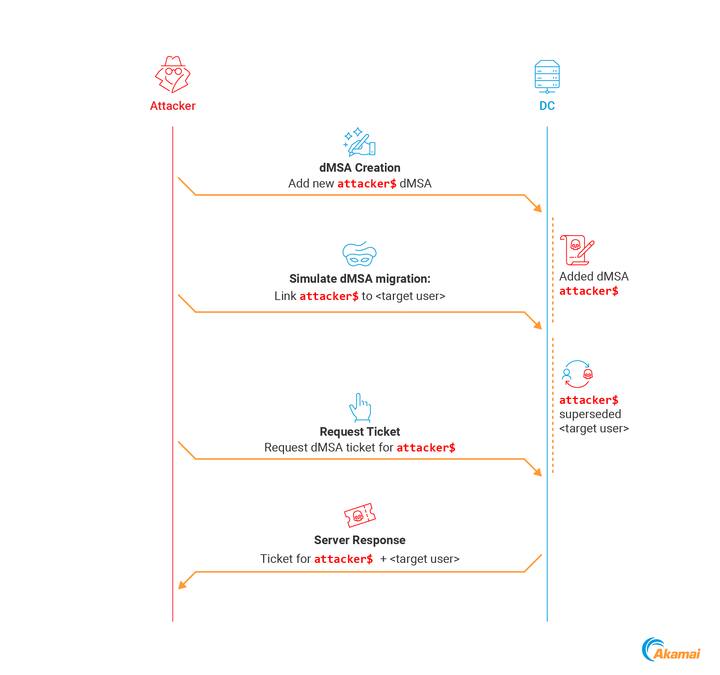
Attackers with write access to specific dMSA attributes can set the msDS-ManagedAccountPrecededByLink and change msDS-DelegatedMSAState, effectively “simulating” a migration.
Subsequently, the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) grants the dMSA all the permissions and group memberships of the targeted account, without actual group modifications or obvious audit trails.
Remarkably, the attack does not require prior compromise of the victim user account. Any user able to create a dMSA within an organizational unit (OU) they control can leverage this vector.
Akamai found that in 91% of environments reviewed, at least some non-admin users possess the necessary permissions, magnifying operational risk.
This flaw empowers an attacker with the permission to create dMSA objects to become any user in the domain, including the ability to escalate to Domain Admin. The attack also enables the inheritance of cryptographic keys, making credential compromise possible on a wide scale.