Top Ransomware Attack Vectors and Prevention: Remote Access Compromise, Phishing, Social Engineering, and Rapid Flaw Exploitation
- Remote Access Dominance: Remote access compromise has emerged as the leading entry point for ransomware, exploiting stolen VPN credentials and OAuth tokens.
- Human-Targeted Tactics: Phishing and social engineering remain pervasive, evolving beyond email to include voice calls and internal collaboration platforms like MS Teams.
- Rapid Exploitation Window: Threat actors often weaponize newly disclosed software vulnerabilities within 24 hours, necessitating accelerated patch management cycles.
Ransomware attack vectors are increasingly sophisticated. Recent industry analysis said attackers are shifting their focus toward cloud-based compromises and human-targeted tactics, with remote access compromise, social engineering, phishing, and the quick exploitation of newly revealed flaws topping the list.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing remains a formidable threat, as campaigns now leverage every available communication channel, including SMS, phone calls, and internal collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, the latest Veeam report said.
Social engineering has expanded into collaboration platforms, and among the common tactics are:
- Emails and Callback Scams – Attackers send fake invoices or subscription notices that prompt recipients to call a fake support number, then persuade the target to install remote‑access tools or share sensitive information.
- Fake Invoices and Credential Resets – Many campaigns, including those by Scattered Spider, impersonate employees who contact help desks or IT support, and require multi-factor authentication (MFA) or password token resets due to allegedly losing phones or credentials.
- Internal Messaging Impersonation – Attackers compromise external Microsoft tenants, often third-party, to contact enterprise users directly via MS Teams or similar tools. They pose as IT support to manipulate the target into installing remote access utilities or approving requests.
Remote Access Compromise
A critical finding indicates that remote access compromise is now the primary entry point for many ransomware attacks. These generally focus on reusing stolen credentials against VPNs or SaaS portals that lack MFA and abusing tokens or integrations, such as compromised OAuth tokens from third‑party SaaS integrations.
They also exploit edge devices such as unpatched VPNs or virtual desktop servers within hours of a vulnerability disclosure.
“While Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is less frequently exposed on the perimeter today, the broader category of remote access compromise includes VPN gateways, virtual desktop solutions, and cloud‑based applications such as Salesforce or Microsoft 360,” the report said.
However, attackers also use the ClickFix approach, deceptive websites, and drive‑by downloads. ClickFix mimics CAPTCHA or bot verification to exploit human behavior, convincing users to run malicious commands. Malicious websites with fake download links, sponsored ads, or search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning trick users into installing malware disguised as legitimate tools, such as Zoom, Putty, or Adobe Reader.
Implementing Cybersecurity Best Practices
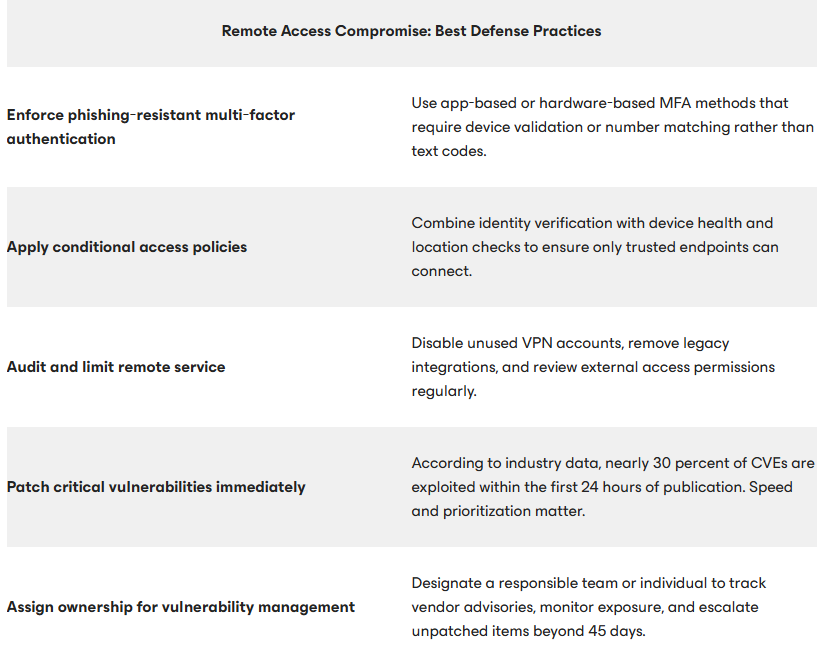
Effective defense relies on foundational cybersecurity best practices. With nearly 30% of CVEs being exploited within 24 hours of publication, organizations are recommended to do the following to prevent exploitation:
- Establish a formal patch management program.
- Assign clear responsibility.
- Use intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS).
- Maintain network segmentation.
- Implement virtual patching for legacy systems.
- Perform post‑patch remediation.
To counter remote access compromise, organizations must enforce phishing-resistant MFA and implement strict conditional access policies that verify device health and location before granting network access.
Phishing prevention now requires defending against multi-channel campaigns that leverage chat applications and voice impersonation to bypass traditional security perimeters. Furthermore, defense strategies must include maintaining air-gapped, immutable backups, which serve as the final line of defense.
While the ErrTraffic ClickFix tool industrializes social engineering malware, a free ClickFix Hunter tool appeared this month.