Scattered Spider Reportedly Deploys DragonForce Ransomware, CISA Advisory Notes Enhanced TTPs
- New TTPs: Scattered Spider displays more sophisticated social engineering techniques, reportedly adding a DragonForce ransomware variant.
- Additional approaches: The update refers to the threat actor searching for Snowflake access, as well as monitoring Slack and Teams communications.
- Enhancements: Moving away from broad phishing campaigns, they employ more targeted and multilayered spearphishing and vishing operations.
The Scattered Spider group, a notorious cybercriminal entity linked to extensive ransomware attacks, changed its tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), adding a DragonForce ransomware variant to their malware arsenal, among others.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), in collaboration with international partners, has issued an updated cybersecurity advisory.
Scattered Spider Tactics and Recent Activities
Scattered Spider is known for employing social engineering techniques to infiltrate organizations. Their methods include phishing emails, push bombing, and SIM swapping to compromise credentials and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems.
The advisory says Scattered Spider targets organizations' Snowflake access to rapidly exfiltrate data via thousands of queries. CISA said trusted sources revealed recent incidents show that the threat actors may have deployed DragonForce ransomware, encrypting VMware ESXi servers. Notably, Scattered Spider was connected to the Snowflake data theft incident in June 2024.
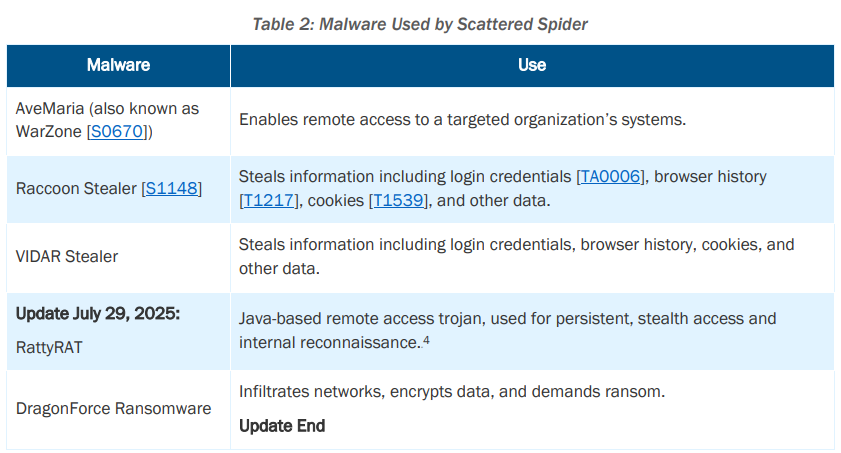
CISA added DragonForce and RattyRAT to the previously known infostealers Raccoon Stealer and Vidar Stealer and remote access tool WarZone.
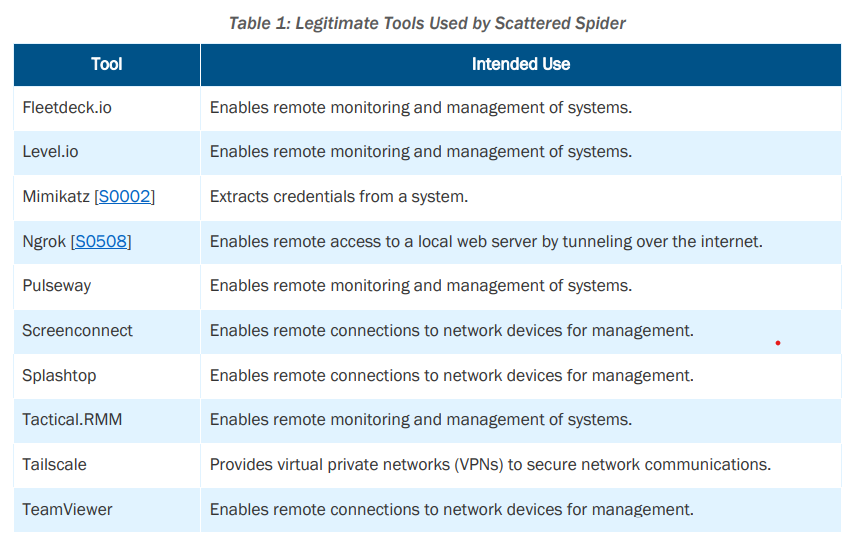
The threat actor also added newly legitimate tools:
- Teleport[.]sh
- AnyDesk
Scattered Spider often checks the target’s Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Microsoft Exchange Online for conversations regarding its intrusion, frequently joining incident remediation and response calls and teleconferences. The update mentions that threat actors sometimes create new identities in the environment, often backed by fake social media profiles.
Despite frequently tweaking their TTPs to evade detection, certain methods have remained consistent.
Scattered Spider threat actors currently gain initial access to a targeted organization’s network in various ways, including illicit marketplaces, credential purchases, such as Russia Market, and compromising third parties working with the targeted organization.
The group’s TTPs include gathering personal and organizational data from business websites, social media, and database leaks. Using social engineering techniques, including SIM swaps and spearphishing calls, they manipulate IT help desks to reset passwords or transfer MFA tokens, enabling account takeovers in SSO environments, the advisory added.
The recent Allianz Life data breach, attributed to social engineering targeting a third-party CRM service, shares similarities with the methods used by the Scattered Spider. However, Agnidipta Sarkar from ColorTokens believed it could also be ShinyHunters.
TechNadu reported in May that a DragonForce ransomware attack leveraged LockBit and Conti TTPs.
Key Mitigation Recommendations
The CISA cybersecurity advisory emphasizes actionable measures that organizations can adopt to mitigate risks posed by the Scattered Spider group. Recommendations include MFA implementation, advanced email filtering, regular audits, and test and response plans for ransomware scenarios.