Novel AV Killer Malware Exploits Legitimate Driver ThrottleStop.sys, Targets All Major Antivirus Solutions
- New cybersecurity threat: The aptly named AV Killer malware exploits a flaw in a legitimate driver to bypass AV solutions.
- BYOVD technique: Attackers abuse exposed I/O control codes to access kernel-level functions directly, hijacking the driver.
- AV Killer targets: The malware attempts to disable almost all major antivirus products on the market.
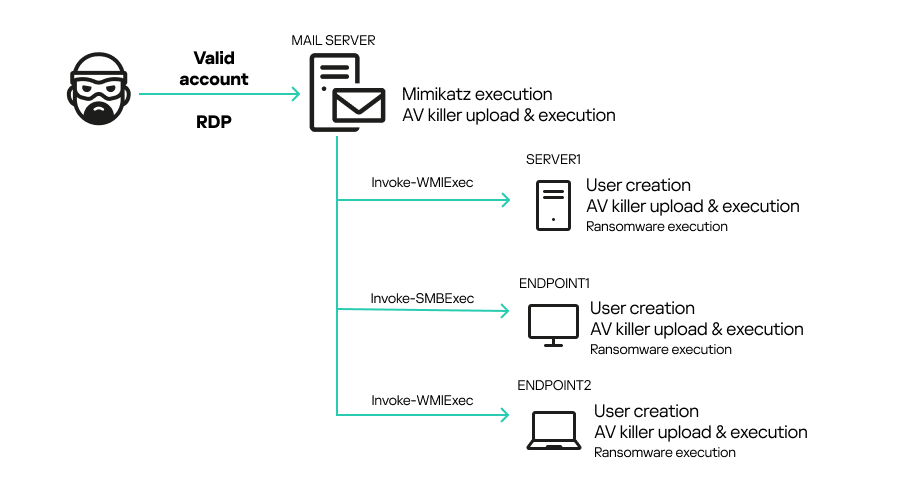
A newly identified cybersecurity threat, known as the AV Killer malware, exploits a vulnerability in the ThrottleStop.sys driver. This antivirus bypass method leverages a Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) technique to disable critical antivirus (AV) processes and compromise system defenses.
Exploitation Method
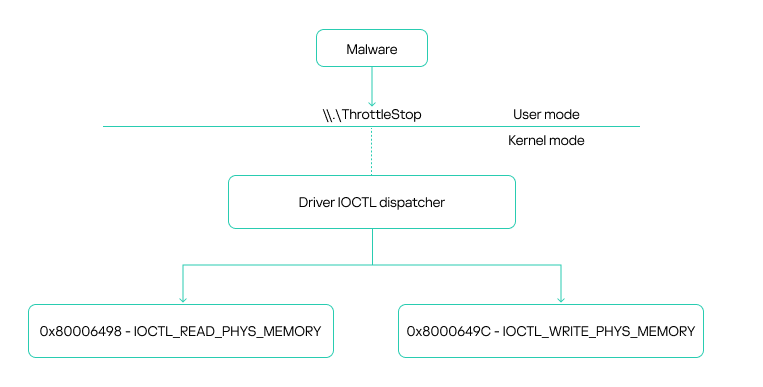
The malicious activity exploits vulnerability CVE-2025-7771 in ThrottleStop.sys, a driver designed by TechPowerUp to address CPU throttling issues.
Attackers exploit the exposed I/O control codes to access kernel-level functions directly, enabling them to read or write memory addresses, according to a recent report by Kaspersky’s SecureList initiative.
Using this flaw, the AV Killer malware hijacks the driver's capabilities to terminate running antivirus software processes, including popular solutions from Microsoft, Avast, McAfee, Kaspersky, BitDefender, and CrowdStrike.
This process achieves a seamless bypass of security defenses, leaving target systems exposed to secondary ransomware attacks, such as MedusaLocker in a recent case. The malware also obscures its activities by creating fake usernames and distributing components like drivers and binaries to network endpoints.
Impact
The AV Killer's ability to disable multiple AV solutions poses serious concerns for both enterprises and individual users. Key regions identified as primary targets include Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, and Brazil, though the technique's flexibility suggests broader applicability.
Cybersecurity Recommendations
To mitigate risks, organizations should enforce whitelisting, strict least‑privilege access, and network segmentation and isolation. Additionally, restrict public-facing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) access, and employ multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all remote connections.
TechPowerUp is reportedly working on a patch for the ThrottleStop.sys vulnerability, marking an essential step in closing this exploitation vector.