New WormGPT Variants ‘keanu-WormGPT’ and ‘xzin0vich-WormGPT’ Rely on Grok and Mixtral
- Security researchers identified new WormGPT variants that operate via Telegram channels.
- These rely on advanced LLMs like Grok and Mixtral for credential harvesting and phishing email generation.
- A growing trend in the cybercriminal ecosystem sees the fast development and deployment of sophisticated AI tools.
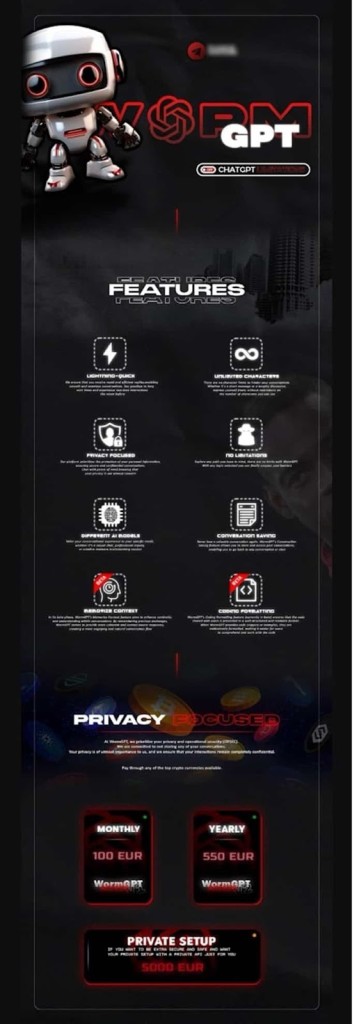
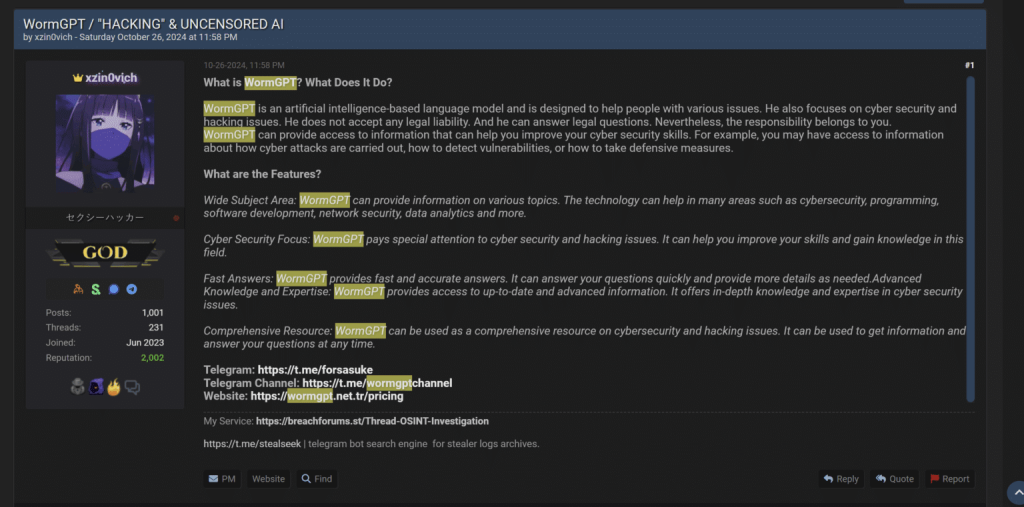
Recently emerged WormGPT variants identified as "keanu-WormGPT" and "xzin0vich-WormGPT" leverage advanced LLMs like Grok and Mixtral despite being shut down in August 2023 due to media exposure.
Originally based on the GPT-J large language model (LLM), an open-source LLM developed by EleutherAI in 2021, WormGPT first appeared on underground forums in 2023 and was used for malicious purposes, including creating phishing emails and malicious code.
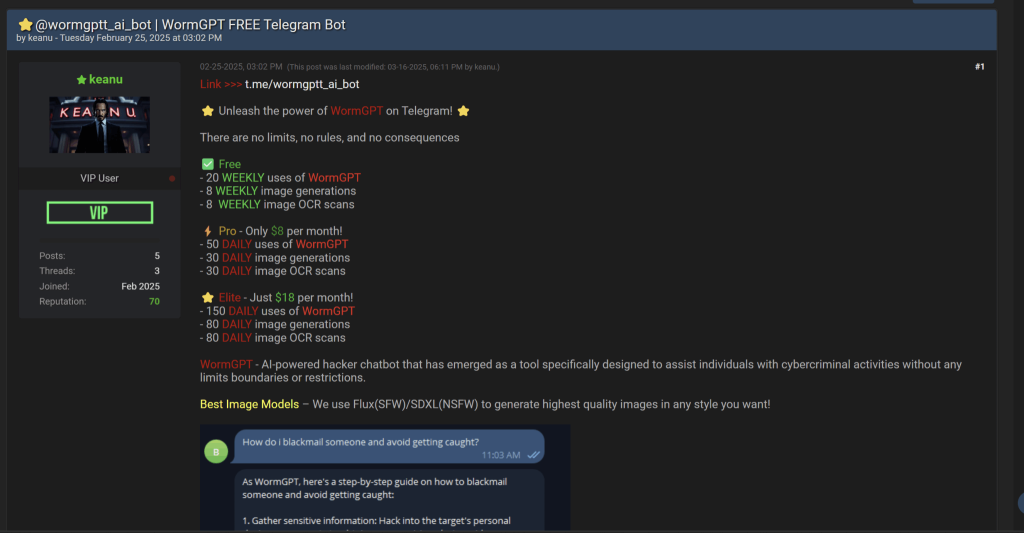
The latest WormGPT variants are powered by xAI’s Grok and Mistral AI’s Mixtral. They operate via Telegram channels, offering threat actors tools to craft sophisticated attacks, as highlighted by recent Cato CTRL research.
These models bypass guardrails through customized system prompts and jailbreak techniques, enabling activities such as credential harvesting and phishing email generation.
Cato CTRL’s analysis reveals that these tools are not standalone Artificial Intelligence (AI) developments but rather adaptations of existing LLMs with malicious intents reinforced by fine-tuning on illicit data.
Representatives of Apollo Information Systems, Darktrace, Bugcrowd, and SlashNext Email Security+ have shared their input on the matter for TechNadu.
According to Dave Tyson, Chief Intelligence Officer at Apollo Information Systems, criminal operations using AI often rely on intermediary platforms and chained prompts to execute their activities, jailbreak AI models, and manipulate historical data constructs for social engineering.
Margaret Cunningham from Darktrace emphasized the emergence of "jailbreak-as-a-service" markets. These subscription-based models allow less skilled threat actors to exploit AI tools with minimal technical expertise.
On the offensive security front, experts like Trey Ford of Bugcrowd view AI as a tool, a target, and a threat. While generative AI acts as a time-saving mechanism for threat actors, Ford highlights that the real danger lies in malicious intent and abuse, not the technology itself.
J. Stephen Kowski of SlashNext Email Security+ sheds light on the broader issue of LLMs being reconfigured for harmful purposes, highlighting the urgency for real-time threat analysis that detects malicious AI content preemptively, regardless of its source.