The Lazarus Group Turns its Attention to Apple Users With a New MacOS Trojan
- A new two-stage malware from the Lazarus group is going after crypto-coin exchanges.
- The malicious software was developed to trick macOS users, and it can currently bypass detection on most AV tools.
- The C&C is currently online, but for now, it is not delivering the second and main payload.
Researcher and threat analyst Dinesh_Devadoss has discovered a new piece of Lazarus malware that was created to target macOS systems. The reason why this new Trojan is connected with the Lazarus group is that it tries to trick the user into believing that it’s a legitimate cryptocurrency app (UnionCryptoTrader.dmg), and we’ve seen this tactic from the North Koreans before. The victim is installing and running the malicious software, which then downloads a secondary payload which is a spying and data exfiltration tool. Nothing is installed on the hard drive, so the whole action is running within your computer's memory.
Another #Lazarus #macOS #trojan
md5: 6588d262529dc372c400bef8478c2eec
hxxps://unioncrypto.vip/Contains code: Loads Mach-O from memory and execute it / Writes to a file and execute it@patrickwardle @thomasareed pic.twitter.com/Mpru8FHELi
— Dinesh_Devadoss (@dineshdina04) December 3, 2019
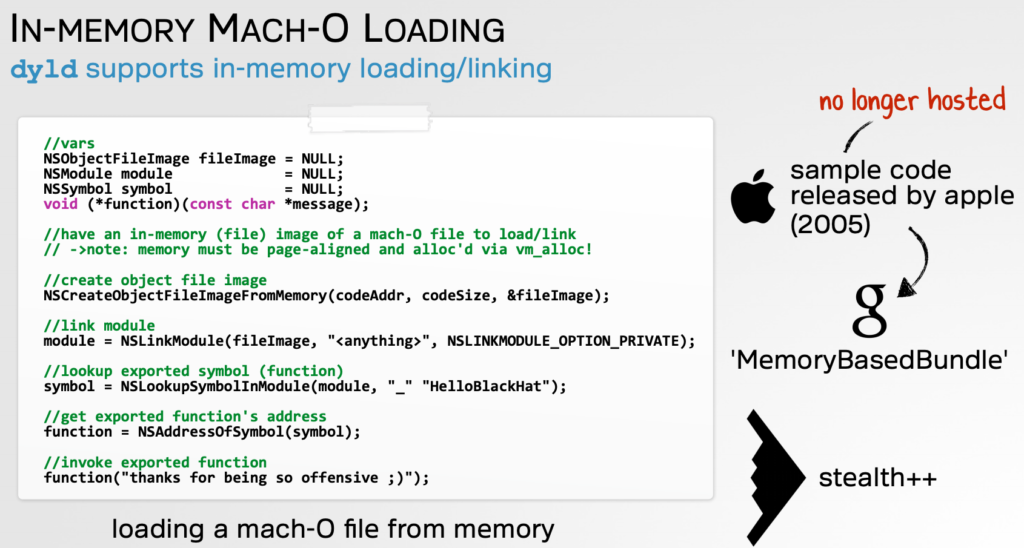
Going a bit deeper into the technicalities, the malware downloads the second payload onto the victim’s machine and decrypts it. Then, through the use of certain macOS API calls, an object file image is created. This helps in laying the ground for the file to run in the memory, simulating an actual installation on the hard drive. At this time, the malware is detected only by a handful of engines, with the majority failing to flag the Trojan. The payload binary is unsigned though, so macOS will serve a warning to the user when trying to run the package.
Source: objective-see.com
The malicious file theming indicates that the Lazarus group is going after crypto-currency exchanges this time. The name "Union Crypto Trader" and the website that has been set up for the purpose of the distribution is in alignment with this assumption. According to Patrick Wardle’s in-depth analysis, the website is still online and querying the IP address (104.168.167.16) is indicating that the Trojan has already been downloaded at least once.
Source: objective-see.com
To establish persistence, the malware plants the "vip.unioncrypto.plist" in the launch daemon, so the binary is launched upon every system boot. The file and the newly created directory is set to be owned by root. The first payload is the "identifier" which can send basic system information back to the actor and retrieve new payload samples from the C2. The stage-2 implant is the main data exfiltrator and the fully-fledged malware of the operation. Unfortunately, the analyst couldn’t get a sample from the C&C, as the server is currently answering back with a zero string. That said, the purposes of Lazarus are unclear right now, but the development of this tool gives us an indication of the focus of the hacking group.
Would you trust any cryptocurrency exchange tool you will find online, or do you prefer something specific? Let us know where you stand in the comments down below, or join the discussion on our socials, on Facebook and Twitter.