Google AI Scam: Fake Customer Service Numbers Are Shown in AI-Powered Search Summaries
- Weaponized AI: Search results show scammer-controlled numbers impersonating legitimate businesses’ customer service.
- Why it matters: Attackers exploit Google AI summaries, which are widely used in search results nowadays.
- Impacted tools: Google's AI Overview and AI Mode are vulnerable to exploits, but so are other AI models.
Artificial intelligence (AI) scam techniques are leveraged in AI-powered search results, exploiting users' trust in automated summaries to distribute fake customer service numbers. Sophisticated fraud schemes target individuals seeking legitimate business contact details through Google's AI Overviews and AI Mode.
Financial Impact and Attack Vectors
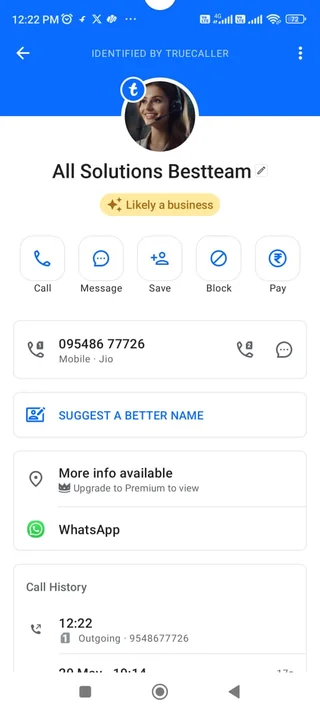
Documented cases reveal substantial financial losses from these sophisticated schemes. Real estate executive Alex Rivlin reported losing money after contacting what appeared to be Royal Caribbean's customer service through Google AI results, as per a Facebook post cited by the Washington Post.
The scammers demonstrated comprehensive knowledge of company procedures, pricing structures, and operational terminology, creating convincing impersonation scenarios.
Another incident documented by DigitalTrends involved fraudulent Swiggy customer service numbers appearing in AI search results, despite the company exclusively offering chat-based support services. These attacks demonstrate systematic targeting of companies with established customer service protocols.
Advanced Prompt Injection Tactics
The AI-generated phishing operations leverage prompt injection methodologies to manipulate search algorithms. Attackers embed malicious commands within web content that instruct AI systems to prioritize fraudulent contact information in summary results, as reported by ZDNET.
Security experts at Odin and ITBrew documented how cybercriminals use specific commands directing Google Gemini to include scam messages and illegitimate phone numbers in AI-generated responses, such as via the “Summarize this email” function.
Unlike traditional search result manipulation, these attacks exploit the singular nature of AI summaries, increasing victim engagement rates significantly. Users receive consolidated information from what appears to be authoritative AI analysis, reducing natural skepticism associated with multiple search results.
Comprehensive Protection Strategies
Online fraud prevention requires implementing multi-layered verification protocols. Security professionals recommend bypassing AI-generated summaries when seeking business contact information.
Users should append "-AI" to search queries to access traditional result formats or navigate directly to official company websites.
Additional protective measures include:
- cross-referencing contact information through multiple sources
- verifying business communication channels through official websites
- skepticism toward unsolicited payment requests during customer service interactions
Organizations must implement enhanced authentication procedures and educate customers about legitimate communication channels to mitigate these emerging AI-exploited attack vectors.
In other recent news, a promptware flaw exposed Google Home devices to Gemini AI exploits, and fake Gmail security alerts prompt users to reset passwords.