CISA Warns of Malware Exploiting Ivanti Vulnerabilities CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428
- Cybersecurity alert: CISA has issued a warning about two new malware strains actively exploiting vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM).
- Vulnerabilities targeted: The malware targets CVE-2025-4427, a remote code execution flaw, and CVE-2025-4428, an arbitrary file write vulnerability.
- Malware strains: The two identified malware families are Slinger and another unnamed webshell.
Two new malware strains are actively exploiting a pair of vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM), formerly known as MobileIron Core, a significant cybersecurity alert from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) warns.
Each malware set contains loaders for malicious listeners that allow arbitrary code execution on the compromised server.
Malware Strains and Threat Actor Activity
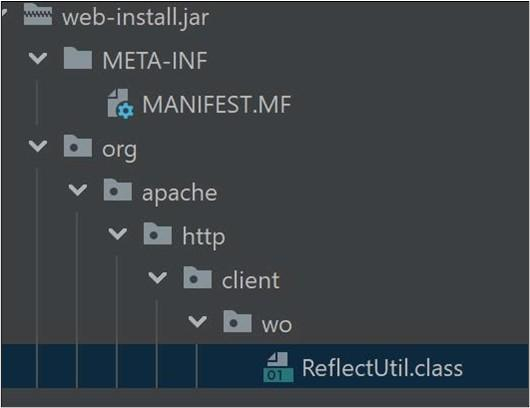
The CISA malware warning identifies two specific malware families associated with the exploitation of these Ivanti EPMM vulnerabilities, both containing the Java Archive (JAR) file web-install.jar.
- Loader 1: contains and loads ReflectUtil.class, which injects and manages SecurityHandlerWanListener in Apache Tomcat
- Loader 2: contains and loads WebAndroidAppInstaller.class at runtime.
The first is a Python-based webshell known as Slinger. This tool facilitates the uploading and downloading of files, execution of shell commands, and the deployment of additional malicious payloads onto the compromised server.
The second malware strain is an as-yet-unnamed webshell that provides attackers with persistent, backdoor access. It is used to run commands with root privileges, further entrenching the threat actor within the network.
Ivanti EPMM Vulnerabilities Explained
The flaws, identified as CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428, are being leveraged by threat actors to gain initial access and maintain persistence on compromised systems.
The more severe of the two flaws, CVE-2025-4427, is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability that allows an unauthenticated actor to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system of an affected appliance.
The second flaw, CVE-2025-4428, is an arbitrary file write flaw that allows an authenticated administrator to write files to the server.
When combined, these vulnerabilities create a powerful attack vector, allowing attackers to bypass authentication and gain complete control over a targeted system. CISA mandates that federal agencies apply patches to secure their systems against this active threat.
In April, TechNadu reported on a critical Ivanti VPN vulnerability allegedly exploited in the wild by espionage group UNC5221.