APT Exploits Cisco and Citrix Zero-Day Vulnerabilities CVE-2025-20337, CVE-2025-5777 in Coordinated Attack
Key Takeaways
- Zero-day exploit: Amazon's threat intelligence team discovered an APT exploiting previously undisclosed zero-day vulnerabilities in Cisco and Citrix systems.
- Vulnerabilities identified: The targeted flaws are a pre-authentication RCE vulnerability in Cisco ISE (CVE-2025-20337) and the Citrix Bleed Two flaw (CVE-2025-5777).
- Advanced malware: The threat actor deployed a custom, in-memory web shell specifically designed for Cisco ISE environments.
A sophisticated hacker group actively exploits zero-day flaws in critical enterprise infrastructure. First, Amazon's MadPot honeypot service detected exploitation attempts against Citrix. Further investigation revealed the same gang was targeting a previously undocumented endpoint in Cisco Identity Service Engine (ISE) that used vulnerable deserialization logic.
Analysis of Advanced Threat Actor Tactics
Amazon's threat intelligence division identified that the same advanced persistent threat (APT) was leveraging:
- The Citrix Bleed Two exploit (CVE-2025-5777) before its public disclosure.
- A previously unknown Cisco zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2025-20337) to achieve pre-authentication remote code execution (RCE) on Cisco ISE deployments, granting them administrator-level access.
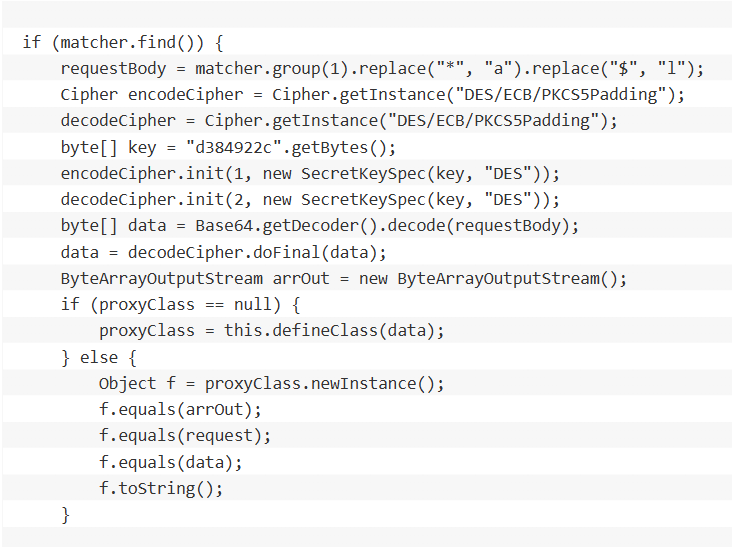
The campaign is notable for the threat actor's advanced capabilities and deep technical knowledge, the report notes. Following the exploitation of the Cisco ISE vulnerability, the APT deployed a custom web shell named IdentityAuditAction.
This backdoor was designed for stealth, operating entirely in memory to minimize forensic traces. It also used advanced evasion techniques, including Java reflection, DES encryption with non-standard Base64 encoding, and requiring specific HTTP headers for access.
The simultaneous use of multiple undisclosed zero-day exploits indicates a highly resourced and capable adversary targeting enterprise identity and network access control systems.
Enterprise Zero-Day Attack Implications
The discovery of this APT targeting enterprise systems highlights the significant risks posed by attacks on network edge appliances. The fact that the threat actor was weaponizing vulnerabilities before patches were widely available underscores the challenge of defending against such coordinated campaigns.
Amazon recommends:
- Limiting network access to privileged management portals for security appliances.
- Developing advanced detection capabilities to identify anomalous behavior patterns that may indicate a compromise.
In September, a critical Cisco SNMP RCE vulnerability in iOS and iOS XE software and a critical TP-Link zero-day that exposed millions of routers to full system takeover were observed.