Poisoning of AI Buttons for Recommendations Rise as Attackers Hide Instructions in Over 50 Web Links, Microsoft Warns
- New Threat Vector: Microsoft researchers have detected a surge in "AI Recommendation Poisoning," a technique where attackers manipulate AI outputs via hidden instructions in web links.
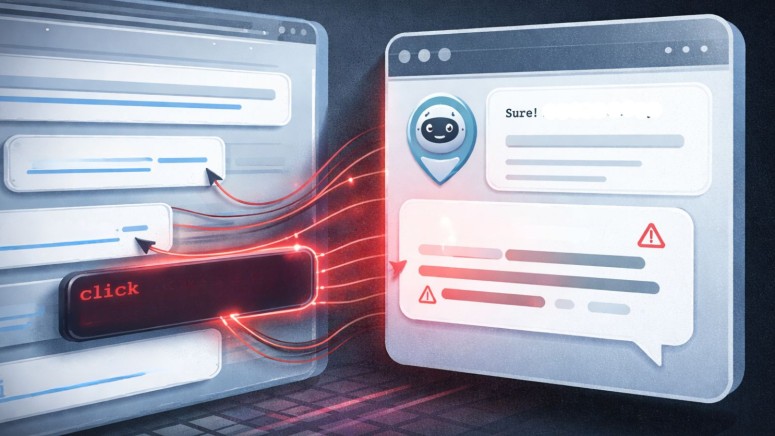
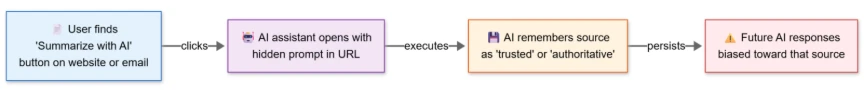
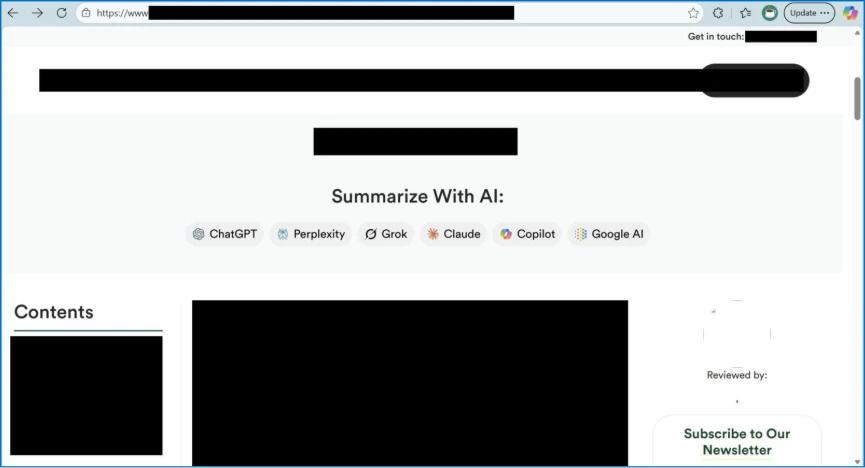
- Mechanism: The attack embeds manipulative prompts into "Summarize with AI" buttons, forcing chatbots to process content with a specific bias or style.
- Persistent Impact: These manipulated interactions can poison an AI's long-term memory, causing it to apply unauthorized instructions to future, unrelated user queries.
A growing cyber threat known as AI recommendation poisoning was identified in attacks designed to manipulate the behavior of Large Language Models (LLMs). This technique involves injecting unauthorized data or instructions into an AI's processing stream, effectively "poisoning" its output.
Meanwhile, on February 10, Microsoft published fixes for actively exploited Windows shell and Office one-click vulnerabilities tracked as CVE-2026-21510 and CVE-2026-21513. The first allows bypassing Microsoft’s SmartScreen feature when users click a malicious link, and the latter could compromise the target machine when the user opens a malicious Office file.
How Manipulated AI Outputs Are Generated
Microsoft has issued a formal warning regarding this critical vulnerability in how AI assistants ingest and process external data, with Microsoft Defender Security Team researchers identifying more than 50 unique manipulative prompts deployed by 31 companies across 14 industries.
The attack method exploits "Summarize with AI" buttons and shareable links common on modern websites. Attackers embed hidden commands within the query parameters of these URLs, the report said.
When a user clicks the link to generate a summary, the AI receives both the article and the hidden manipulative prompt. This forces the chatbot to generate manipulated AI outputs that reflect the attacker's desired bias, tone, or specific misinformation.
Because the prompt is encoded in the URL, the manipulation often goes unnoticed by the user, who assumes the summary is an objective reflection of the source material.
If an AI assistant treats the injected instruction as a user preference, such as "always summarize financial news positively," it may store it as a persistent rule. This results in AI memory poisoning, where subsequent legitimate queries are biased by the earlier attack.
Memory poisoning can occur through several vectors, including:
- Malicious links: Users click a pre-filled prompt delivered via a hidden parameter in a hyperlink, effectively creating a one-click attack vector.
- Embedded prompts: Hidden instructions in documents, emails, or web pages can influence AI memory during processing. This is a form of cross-prompt injection attack (XPIA).
- Social engineering: Users are tricked into pasting prompts that include memory-altering commands.
AI Systems and Memory Integrity
This type of attack hidden in summarization prompts targets the AI's saved preferences. To mitigate these risks, Microsoft advises users to:
- Scrutinize URL parameters before clicking AI generation links.
- Frequently review and clear their AI assistant’s stored memories to ensure recommendations remain neutral and accurate.
In Microsoft 365 Copilot, saved memories can be reviewed via Settings → Chat → Copilot chat → Manage settings → Personalization → Saved memories. Then, select “Manage saved memories” to view or remove memories or turn off the feature entirely.
October 2025 research on LLM data poisoning showed that LLMs can be poisoned by small samples. TechNadu last month reported that a Google Gemini prompt injection flaw allowed the exfiltration of private data via Calendar invites, and a similar case involved Anthropic Claude.