AI-Powered Phishing Accelerated to One Attack Every 19 Seconds in 2025, Report Reveals
- Rapid Escalation: In 2025, the frequency of malicious email attacks more than doubled, reaching a pace of one attack every 19 seconds.
- Polymorphic Threats: 76% of initial infection URLs and 82% of malicious files identified were unique, rendering traditional pattern-matching defenses ineffective.
- Weaponized Tools: The abuse of legitimate remote access tools, such as ConnectWise ScreenConnect, surged by 900% as attackers leveraged trusted infrastructure.
AI-powered phishing attacks now occur every 19 seconds, up from one every 42 seconds in 2024. This spike signals that artificial intelligence (AI) has transitioned from an experimental tool to a core operational requirement for threat actors.
This escalation was documented in the latest Cofense phishing report, titled “The New Era of Phishing: Threats Built in the Age of AI,” which identifies several critical attack trends defining this new landscape.
Emerging Phishing Attack Trends and Tactics
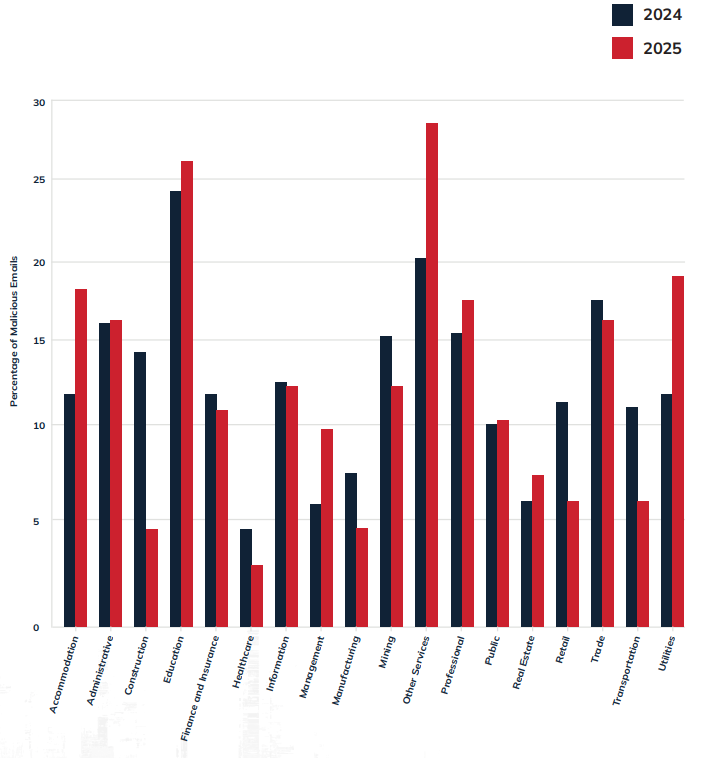
Foremost among them is the normalization of polymorphic attacks as the default delivery model. Attackers now leverage AI to personalize messages using publicly available data, with 76% of phishing attacks using unique initial infection URLs and 82% of malicious files having unique hashes.
Furthermore, threat actors are deploying adaptive, analysis-aware phishing pages that deliver different payloads based on the victim's operating system, and advanced kits detect security tools and redirect analysts to legitimate websites.
As AI has reduced traditional warning signs such as spelling mistakes, business email compromise (BEC) has surged, with conversational attacks now comprising 18% of all malicious emails.
The report also highlights a 900% explosion in the weaponization of legitimate remote access tools such as ConnectWise ScreenConnect, GoTo Remote Desktop, and similar IT management software as remote access trojans (RATs).
Researchers also noted that credential phishing campaigns using .es domains increased 51 times year over year, with the top-level domain (TLD) jumping from 56th to the third most abused, showing how threat actors use “AI-enabled phishing kits that automatically generate domains, deploy subdomains, and launch advanced credential harvesting at scale with minimal human intervention.”
Adapting Cybersecurity Defense Strategies
The integration of AI into the attack lifecycle requires an evolution in cybersecurity defense strategies, as defenses relying on known signatures are no longer sufficient.
The report concludes that organizations must integrate employee-reported intelligence with automated remediation, enabling security teams to identify and neutralize these highly sophisticated, context-aware attacks before they cause significant operational damage.
This month, TechNadu reported on an AI-assisted cloud intrusion compromising AWS environments in 8 minutes, and state-aligned actors that conducted a RedKitten AI-accelerated campaign themed around Iranian protests.
A November report highlighted the rise of malicious AIs, as WormGPT 4 emerged as a powerful tool for cybercrime.