Advanced Phishing Campaign Targets Customers of Major Italian Web Host Aruba S.p.A.
Key Takeaways
- Targeting Italy: A large-scale phishing campaign is actively targeting customers of Aruba S.p.A., one of Italy's largest web hosting providers.
- Sophisticated toolkit: The attackers are using an advanced phishing kit that includes CAPTCHA filtering and pre-filled user data to appear legitimate.
- Telegram integration: The operation relies on Telegram bots for the immediate exfiltration of stolen credentials and payment information.
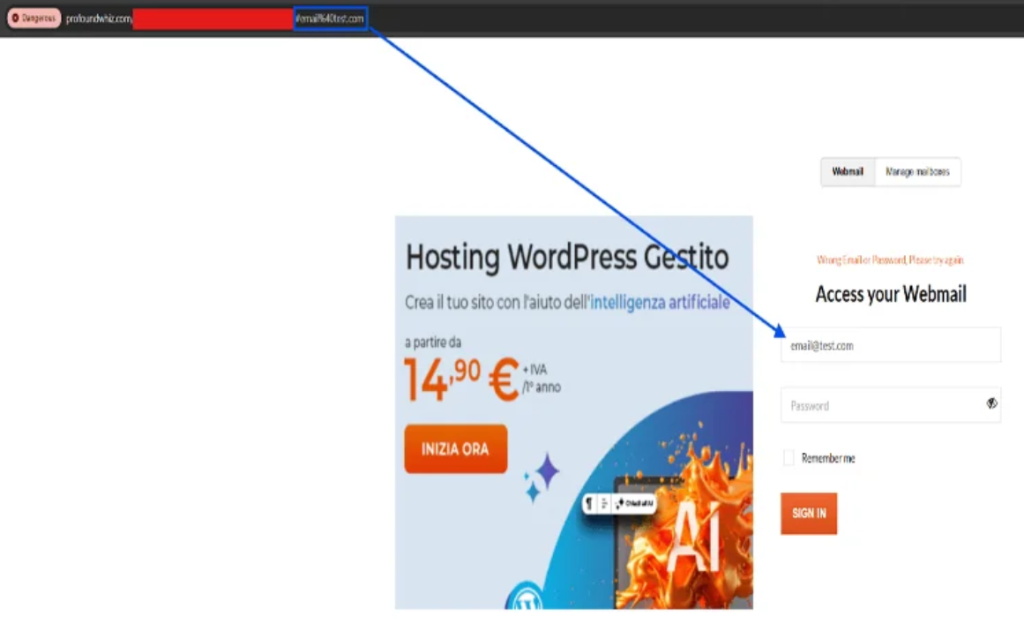
A significant Aruba phishing campaign has been identified, targeting customers of the major Italian web hosting and IT services provider to steal sensitive user credentials and credit card details.
Given that Aruba serves over 5.4 million customers, a single compromised account could expose critical business assets, including hosted websites, domain controls, and corporate email environments.
Phishing Kit with Telegram Bots Deployed
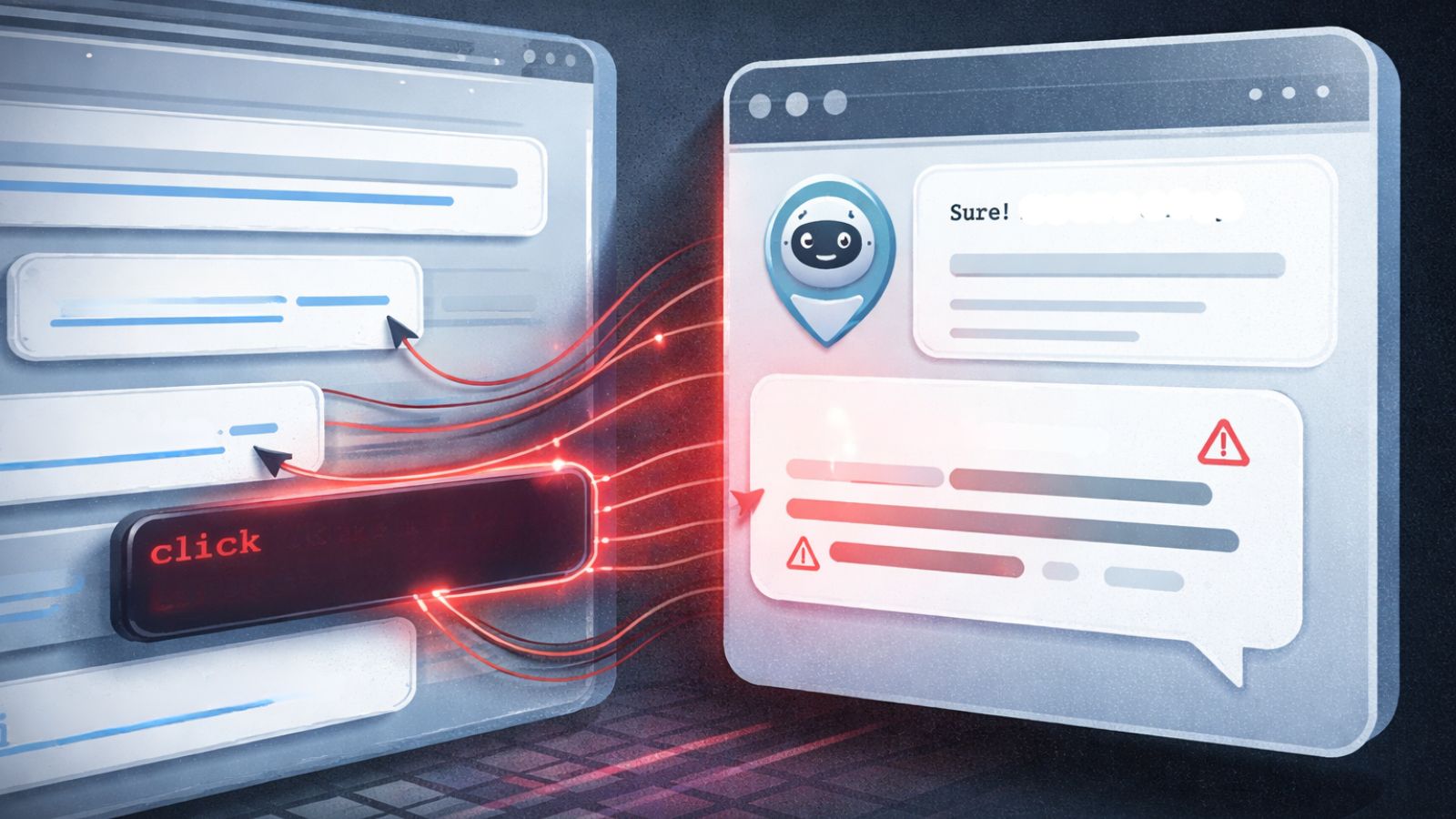
According to a recent Group-IB report, the campaign utilizes a sophisticated phishing kit with Telegram bots, which is being sold as a service to other cybercriminals. Victims are lured via emails about expiring services or failed payments to a fraudulent login page.
- Stage 1: Evasion & Access – The fake website incorporates features like CAPTCHA filtering to evade automated security scanners.
- Stage 2: Credential Theft – The victim's email address is pre-filled to enhance credibility. Once credentials are submitted, they are sent to attackers via Telegram immediately.
- Stage 3: Financial Data Harvesting – A fake payment page for a small, plausible fee steals full credit card details (name, card number, expiration date, CVV).
- Stage 4: 3D Secure/OTP Harvesting – A fake verification page requests the one-time password (OTP) that attackers steal, then redirects users to the legitimate Aruba website.
The phishing operation's reliance on Telegram for coordination and data exfiltration marks a notable level of operational sophistication.
Recommendations for Businesses and End Users
Among the recommendations for organizations and service providers are:
- Implement solutions to filter malicious content and inspect URLs.
- Enforce email authentication standards like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Actively monitor for impersonating domains and phishing sites and request their takedown.
- Use a zero-trust approach.
- Make payments by redirecting to the banks’ official websites for MFA/authorization, and do not host all on your infrastructure.
End users should remain skeptical of any email that uses any social engineering techniques, like creating urgency or fear.
- Always verify the sender and hover over links to check the destination URL before clicking – an HTTPS lock icon does not guarantee a site is legitimate.
- Avoid using any links in suspicious emails from Providers. Instead, open a new browser window and manually log in to your account.
- Enable MFA on your critical accounts. Where available, prioritize passkeys over SMS or app-based OTPs and use a password manager.
Recent reports show that phishing and scam threats are surging in relation to the shopping season and holidays – mobile phishing campaigns are increasing, and over 1,000 websites impersonating luxury brands have been registered.