LLM Side-Channel Attack ‘Whisper Leak’ Exposes Encrypted Communications
Key Takeaways
- New vulnerability: A side-channel attack named "Whisper Leak" can infer the topics of encrypted Large Language Model conversations.
- Attack method: It analyzes patterns in the size and timing of network packets from streaming LLM responses to classify the subject matter of a user's prompt.
- Partial mitigation: Several major LLM providers, including Microsoft and OpenAI, have implemented fixes, but models from other vendors remain unpatched.
A novel LLM side-channel attack may compromise the privacy of encrypted communications with large language models (LLMs). The attack, dubbed "Whisper Leak," allows an observer with network access to infer the topic of a user's prompt, even without decrypting the content.
The attack is effective against streaming models, which send responses incrementally, creating observable patterns in network traffic.
How the Side-Channel Attack Works
The Whisper Leak vulnerability operates by monitoring the metadata of network traffic – specifically, the size and timing of Transport Layer Security (TLS) end-to-end encrypted data packets sent from the LLM back to the user, Microsoft researchers have disclosed.
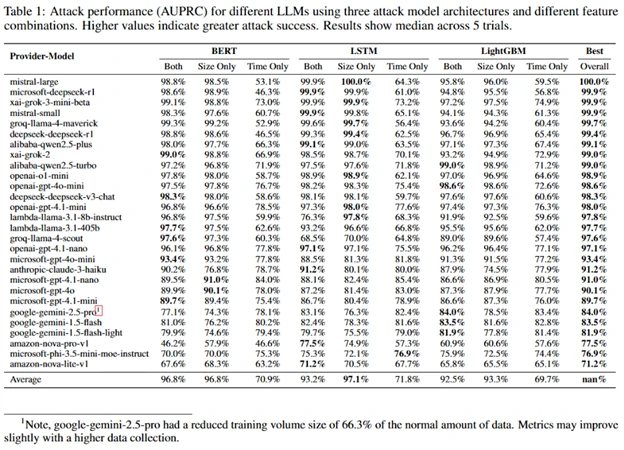
Researchers demonstrated that by training a binary classifier, they could distinguish between conversations on specific topics (e.g., money laundering) and general traffic with high accuracy. The researchers leveraged 11,716 random, unrelated questions from the Quora Questions Pair dataset for negative noise samples.
Three different machine learning models were evaluated after collecting data via AUPRC, which measures a cyberattack’s success for imbalanced datasets, each in three modes (time-only, packet-size only, or both):
- LightGBM: A gradient boosting framework.
- LSTM-based (Bi-LSTM): A recurrent neural network architecture suitable for sequential data.
- BERT-based: Using a pre-trained transformer model (DistilBERT-uncased) adapted with extended tokens representing size and time buckets for sequence classification.
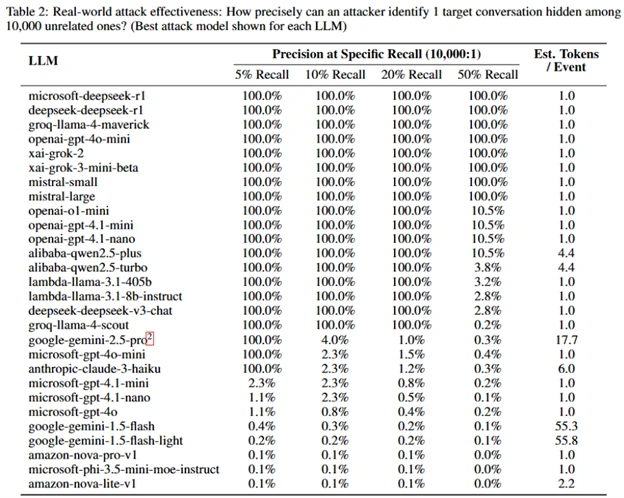
A simulated surveillance scenario imagined a cyberattacker monitoring 10,000 random conversations that included one about the targeted sensitive topic and showed that a cyberattacker could achieve 100% precision.
An attacker in a position to monitor network traffic, such as an internet service provider, government agency, or a bad actor on a local Wi-Fi network, could use this method to surveil user activities, the report adds.
Mitigation and Industry Response
This AI vulnerability raises significant concerns about encrypted communication risks, particularly for users discussing sensitive subjects like proprietary business information, legal matters, or political dissent.
In response to the disclosure, several prominent AI providers, including Microsoft, OpenAI, Mistral, and xAI, have implemented mitigations.
Concerned end users can also:
- Avoid highly sensitive topics with AI chatbots via untrusted networks.
- Use VPNs for an additional layer of protection.
- Use providers with implemented mitigations.
- Use non-streaming LLMs.
This incident underscores the urgent need for AI developers to address not only direct data security but also the more subtle risks posed by side-channel information leakage.
An October report found that LLMs can be poisoned by small samples. Around the same time, an Australian contractor caused a data breach by uploading 3,000 flood victims’ information to ChatGPT.