VoidProxy Phishing-as-a-Service Operation Enables AiTM Attacks Targeting Google, Microsoft Accounts
- AiTM attacks: The newly discovered VoidProxy PhaaS platform enables attackers to steal user credentials.
- Google and Microsoft accounts: Phishing emails sent from compromised providers redirect to fake login pages.
- Session hijacking: Microsoft or Google credentials are sent to VoidProxy’s core AitM proxy server.
A new phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform named VoidProxy is enabling cybercriminals to conduct sophisticated attacker-in-the-middle (AiTM) attacks targeting Google and Microsoft accounts. It provides a turnkey solution for stealing user credentials, multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes, and session tokens in real time.
How the VoidProxy Phishing Service Operates
According to new findings from Okta threat intelligence, the PhaaS operation begins with phishing emails sent from compromised, legitimate Email Service Providers (ESPs) such as Constant Contact, Active Campaign (Postmarkapp), NotifyVisitors, and others.
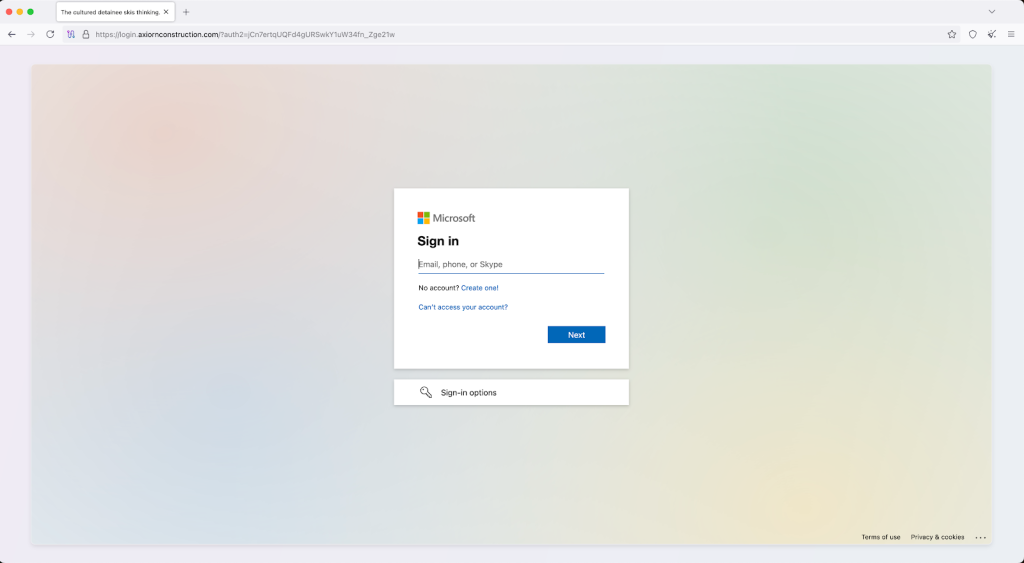
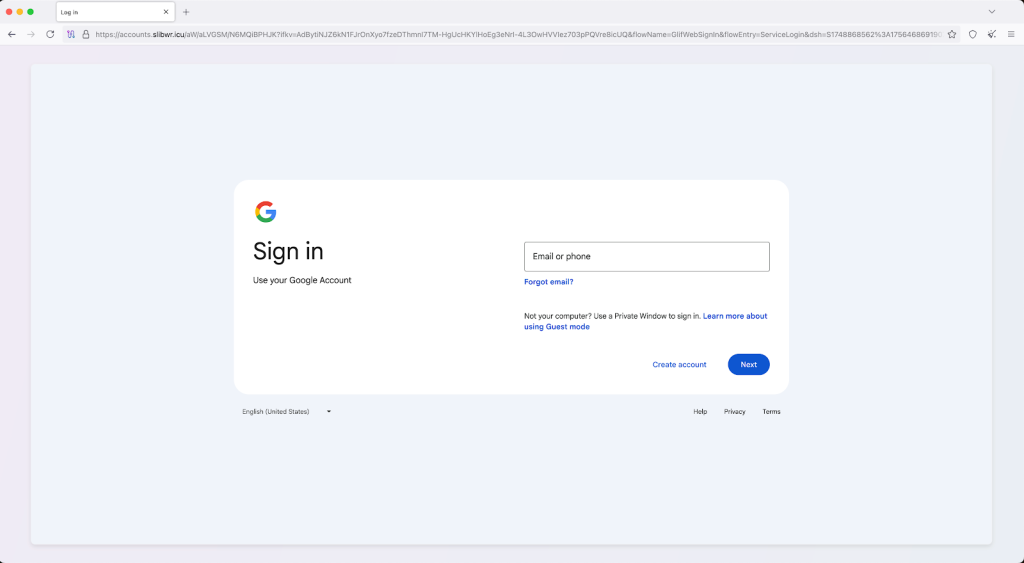
These emails contain shortened URLs that redirect victims through multiple stages before landing on a phishing site that first checks for bots via a Cloudflare CAPTCHA challenge.
The phishing pages perfectly mimic Google or Microsoft sign-in pages and can also redirect accounts protected by third-party single sign-on (SSO) providers like Okta to second-stage phishing pages.
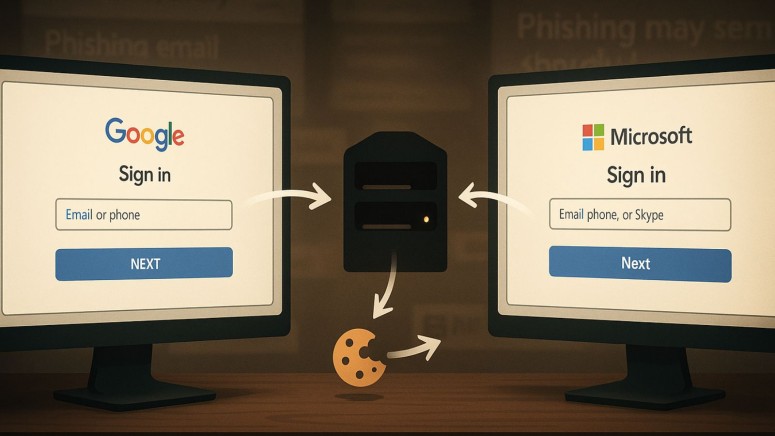
When a user enters their credentials, the information is sent to VoidProxy's AiTM proxy server. This server relays the username, password, and MFA response to the legitimate service for session hijacking.
Once authenticated, the legitimate service issues a session cookie, which is intercepted by the proxy server. A copy of this valid session cookie is then exfiltrated and made available to the attacker through an administrative panel, allowing them to bypass security measures and gain full access to the victim's account.
VoidProxy evades analysis via multiple layers of anti-analysis features, including:
- compromised email accounts
- multiple redirects
- Cloudflare CAPTCHA challenges
- Cloudflare Workers
- dynamic DNS services
Expanding on how VoidProxy differs from earlier phishing kits, Certis Foster, Senior Threat Hunter Lead at Deepwatch, said, "VoidProxy fundamentally is different from previous AiTM phishing kits by hiding inside legitimate infrastructure like (Cloudflare Workers, dynamic DNS) that organizations can’t block without breaking business operations, making it invisible to email gateways and web proxies while successfully bypassing all traditional MFA methods (SMS, OTP, push notifications) only phishing-resistant authentication (FIDO2/passkeys) prevented compromise in attacks reported in the wild."
Security Recommendations and Impact
Highlighting the broader defensive challenge, James Maude, Field CTO at BeyondTrust, explained: "The key thing for security teams is to reduce their identity attack surface. This involves understanding all the paths to privilege that any given identity has in their environment, either intentional or accidental, and reducing that ‘blast radius’ as much as possible."
The VoidProxy phishing service has successfully compromised accounts across multiple industries and geographies. To mitigate the risk of such AiTM attacks and improve Google and Microsoft account security, experts recommend several defensive measures.
“VoidProxy represents a mature, scalable and evasive threat to traditional email security and authentication controls,” said Okta.
Organizations and users should:
- adopt strong, phishing-resistant authenticators like FIDO2 WebAuthn (passkeys and security keys) and smart cards
- enforce phishing-resistance policies that require their use
- automate remediation flows
- deny/require higher assurance for requests from rarely used networks
Continuous monitoring of new infrastructure and enforcing strict industry standards for identity management are also critical for defending against these ongoing threats.
In July, TechNadu reported on PoisonSeed tricking users out of FIDO2, redirecting Microsoft, Google, and Okta logins to phishing pages as per an Expel analysis. CAPTCHA checks were also used on fake Google login pages to steal user credentials recently.