VPS Infrastructure Exploited in Coordinated SaaS Account Compromises
- SaaS phishing: Threat actors leveraged Virtual Private Servers to establish anonymous infrastructure for account takeover operations.
- VPS exploit: A May 2025 campaign, observed by cybersecurity researchers, revealed coordinated VPS abuse in SaaS environments.
- Targets: Hyonix, Host Universal, Mevspace, and Hivelocity are among the targeted VPS providers.
Sophisticated threat actors leverage Virtual Private Server (VPS) infrastructure to execute targeted phishing campaigns against Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) environments, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in enterprise email security protocols.
Advanced Threat Actors Target SaaS Through VPS Networks
Cybersecurity researchers at Darktrace identified coordinated VPS abuse in SaaS environments during May 2025, documenting systematic compromises across multiple customer networks.
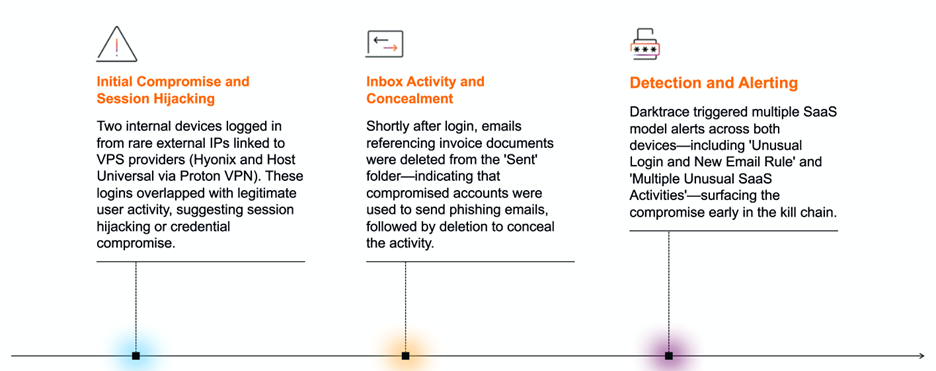
The investigation revealed threat actors exploiting VPS providers, including Hyonix and Host Universal (via Proton VPN), to establish anonymous infrastructure for launching sophisticated account takeover operations.
The phishing campaigns demonstrated advanced tactics involving session hijacking, multi-factor authentication (MFA) bypass, and persistent access maintenance.
Attackers utilized VPS infrastructure to evade geolocation-based security controls while mimicking legitimate user behavior patterns, rendering traditional detection mechanisms ineffective.
“In this case, the adversary is riding live sessions and no longer just harvesting passwords. The mailbox becomes the control plane. Vague rules act like a kind of stealth policy,” said Jason Soroko, Senior Fellow at Sectigo.
Systematic Compromise Methodologies Identified
Darktrace's analysis documented two primary attack vectors targeting enterprise email systems. The first involved coordinated logins from rare VPS-associated IP addresses, occurring within minutes of legitimate user activity from geographically distant locations—a clear indicator of session hijacking attempts.
Following initial access, threat actors implemented persistence mechanisms through manipulated inbox rules with obfuscated names. These rules automatically deleted incoming emails referencing specific documents, effectively concealing malicious activities from legitimate account owners and automated security audits.
A second attack pattern involved similar login activity originating from Hyonix, Mevspace, and Hivelocity as multiple users logged in from rare endpoints successfully verified via MFA, demonstrating a sophisticated understanding of enterprise authentication frameworks.
Investigators observed coordinated spam distribution featuring generic finance-related subject lines, indicating broader campaign objectives beyond simple credential harvesting.
Critical Security Implications for Enterprise Environments
The investigation revealed significant gaps in traditional security architectures when confronting VPS-enabled threats. Attackers successfully bypassed IP reputation checks using clean, newly provisioned infrastructure while maintaining operational security through minimal Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) footprints.
Enhanced Detection and Response Strategies Required
Organizations must implement behavior-based detection systems capable of identifying subtle anomalies, including improbable travel patterns, unusual login sources, and unauthorized mailbox rule modifications.
Cybersecurity measures should encompass continuous monitoring of authentication events, particularly simultaneous sessions from disparate geographic locations.