ClickFix PowerShell Attack Chain Leverages Email Invite Lures, Spoofed MS Teams Login Pages
- PowerShell attack: A PowerShell-based infection chain ultimately disseminates a RAT, executed entirely through PowerShell.
- Attack methods: Phishing emails using professional session invitations as lures lead to fake Microsoft Teams login pages.
- Hackers’ targets: A targeted ClickFix campaign impacted multiple Israeli organizations
A sophisticated ClickFix PowerShell attack chain targeting Israeli organizations leverages phishing tactics, PowerShell scripting, and remote access tools, making it a considerable threat to targeted enterprises, cybersecurity experts have uncovered.
Attack Methodology
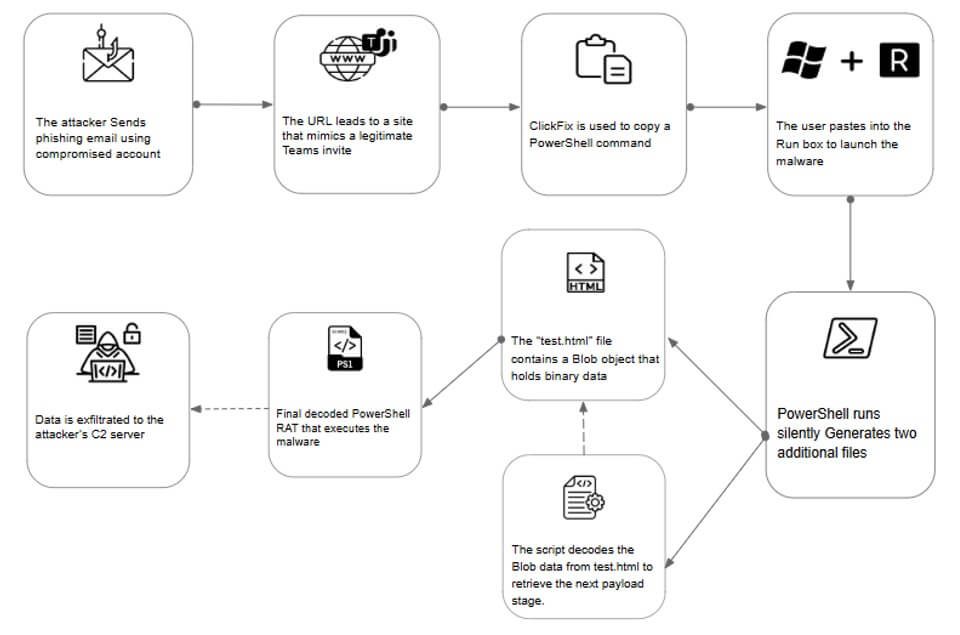
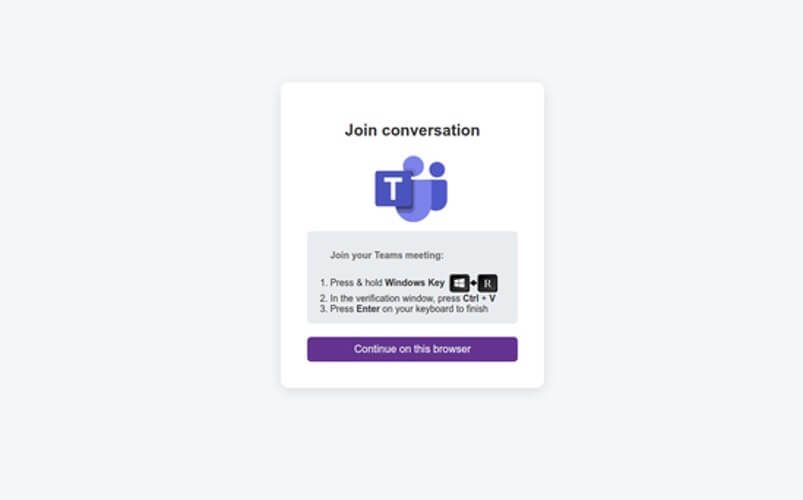
The campaign, as detailed in Fortinet's report, begins with phishing emails masquerading as invitations to mentoring sessions “on handling wartime conditions and the use of medical and pharmaceutical supplies,” urging recipients to engage with a malicious link that directs users to a fake Microsoft Teams portal.
There, the visitors are instructed to execute a Base64-encoded PowerShell command. By leveraging social engineering, the attackers successfully initiate a multi-stage infection process.
The initial malicious script downloads additional payloads from attacker-controlled servers under the guise of system updates.
These payloads deliver a remote access trojan (RAT), granting the threat actors full control over compromised systems. The malware facilitates data exfiltration, lateral movement, and long-term persistence by evading detection through techniques like obfuscated scripting and compressed C2 communications.
Lateral expansion tactics closely mirror those of MuddyWater, and other elements like the infrastructure, regional targeting, and scripting techniques strongly align with previously attributed MuddyWater activity.
Yet, attribution is inconclusive. Fortinet assesses that the payload delivery was distinct, and the actor deliberately avoided using remote management tools (RMMs) or public file-hosting services.
Implications and Risks
The exclusive reliance on PowerShell—a legitimate Windows feature—is a hallmark of advanced cybersecurity threats, making detection highly challenging. Victims risk theft of financial data, intellectual property, and significant business disruption.
Defensive Measures
To counter these advanced tactics, Fortinet emphasizes proactive measures, including network monitoring, endpoint defenses, and staff training on phishing recognition. Implementing Real-Time PowerShell logging and restricting script execution policies can fortify defense lines. Regular patching and updating of security systems further reduce vulnerabilities.
This month, TechNadu reported on the evolution of ClickFix fake CAPTCHA campaigns to cross-platform tactics targeting macOS and Linux.
Organizations are urged to adopt robust cybersecurity strategies to mitigate evolving threats like the ClickFix PowerShell attack chain.