Malicious Telegram APK Campaign Exploits Fake Domains and Android Vulnerabilities
- Attackers utilize advanced phishing to exploit trust in software downloads from familiar-looking websites.
- Security researchers flagged over 600 domains linked to fake Telegram APK files.
- Android users were targeted via typosquatting techniques and redirect QR codes.
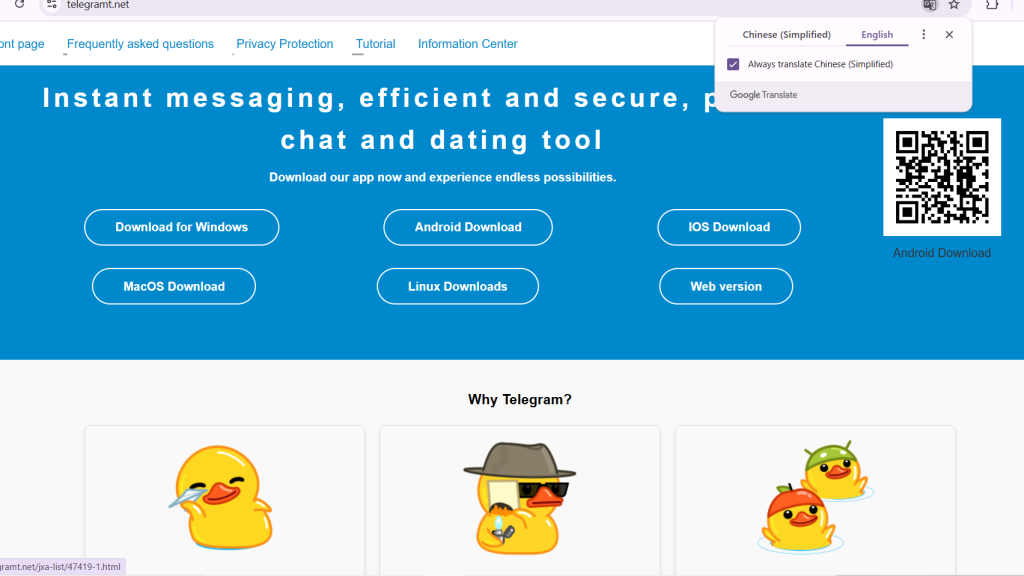
A significant APK phishing campaign targets unsuspecting users with fake Telegram applications. Over 600 domains, primarily hosted in Chinese, have been linked to distributing malicious APK files disguised as legitimate Telegram installations.
Fake Telegram Domains Deceive Users
The attackers employed typosquatting techniques, setting up domains with names resembling Telegram, such as:
- Teleqram
- Telegramapp
- Telegramdl
- Apktelegram
These domains host QR codes that direct victims to a central site, zifeiji[.]asia, designed to mimic the messaging app's official website.
This landing site implements recognizable branding elements like themes and favicons to build credibility, a new cybersecurity report by BforeAI’s PreCrime Labs underscores.
Victims are enticed into downloading APK files approximately 60MB to 70MB in size. Once installed, these apps execute malicious operations while remaining disguised as legitimate.
Exploiting Android Vulnerabilities
The malicious APKs are signed with an outdated v1 signature scheme, making them susceptible to the Janus vulnerability, which affects Android versions 5.0 to 8.0. This security flaw allows tampered apps to bypass modern detection measures by maintaining original signatures.
By leveraging this vulnerability, attackers distribute malware that executes remote commands, steals data, and grants them control over compromised devices.
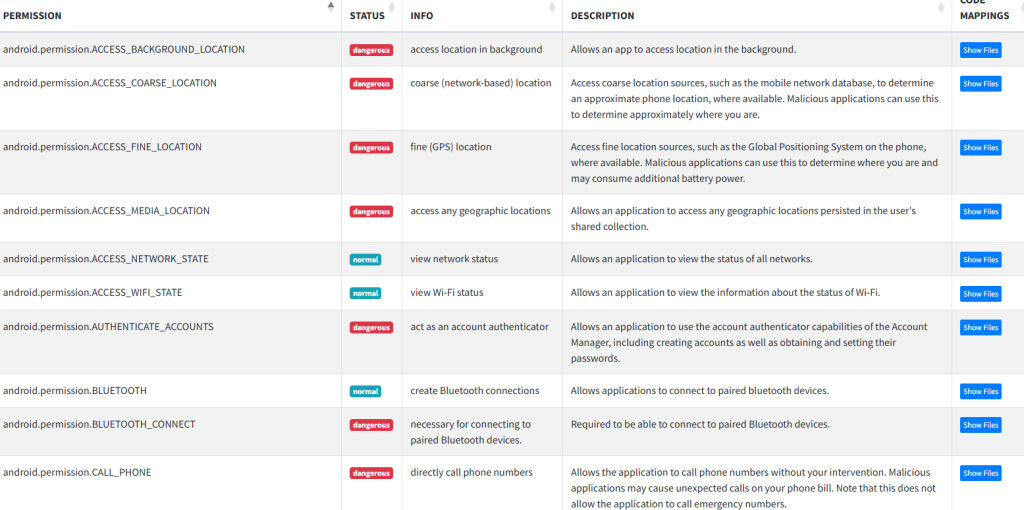
Further, the apps use insecure cleartext protocols such as HTTP and FTP, exposing user data to interception. With broad permissions like accessing external storage, the malicious APKs increase risks of data theft, surveillance, and device manipulation.
Risks Posed and Preventive Measures
This phishing campaign endangers users by compromising their sensitive data, enabling surveillance, and making devices vulnerable to further exploitation. Those relying on older Android systems are particularly at risk due to the exploitable Janus vulnerability.
To mitigate these risks, users and organizations should prioritize security measures, including downloading apps only from verified sources like Google Play, blocking suspicious domains, and regularly updating devices to eliminate vulnerabilities.
Previous Incidents Involving Fake APKs
The malicious Telegram APK campaign is yet another case where attackers target Android users with fake services for phishing purposes. For instance, earlier this year, Indian bank customers were targeted with malicious WhatsApp APKs to steal sensitive user data.