Identity-Centric Threats Relying on Infostealers Dominate the Modern Cybercrime Landscape
- Identity-based attacks are emerging as one of the most dominant and disruptive threat vectors, focusing on credential stealing.
- Cybercrime-as-a-Service platforms increasingly help attackers of varying skills execute advanced campaigns with a low entry barrier.
- Modern infostealers target browser-stored credentials, password manager databases, VPNs, and application-specific tokens.
Identity-centric cyberattacks have surged by an alarming 156% between 2023 and 2025. These attacks now account for 59% of all confirmed threats in Q1 2025, reshaping how organizations must approach security in an era dominated by credential theft and identity exploitation.
Traditional attacks that targeted technical flaws have increasingly been supplanted by sophisticated identity-centric campaigns, where threat actors gain direct access to organizational assets by compromising user identities.
J. Stephen Kowski, Field CTO at SlashNext Email Security+, emphasizes that attackers are targeting the human element “because it’s often the weakest link in security chains.”
At the forefront of this trend is the proliferation of Cybercrime-as-a-Service (CaaS) platforms, including Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) models, a recent report from eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU) says.
Services like Tycoon2FA, which alone account for 58% of observed account compromise cases, are available for as little as $200–$300 USD per month. These platforms provide enterprise-grade credential harvesting capabilities, including advanced Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) functionalities that allow attackers to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
As a result, attackers of varying skill can execute advanced campaigns with a low barrier to entry and potentially high returns, as Will Bailey, Senior Cyber Defender at Ontinue, agrees.
PhaaS criminal organizations often promise support and bypassing anti-phishing controls and spam detection, with generic, easy-to-use templates to steal credentials from popular platforms, Thomas Richards, Infrastructure Security Practice Director at Black Duck, said, reminding how caution is key.
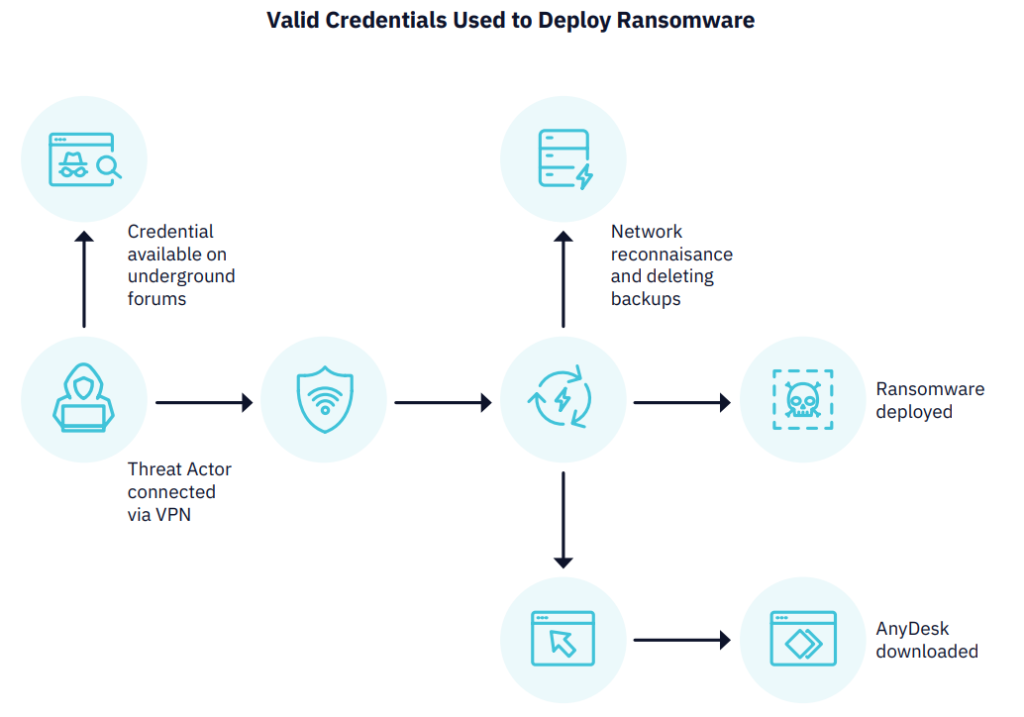
Infostealer campaigns have moved well beyond basic credential theft, evolving into comprehensive identity harvesting platforms. Lumma Stealer, also known as LummaC2, was the most disrupted malware family in 2024 and 2025.
Modern malware now targets browser-stored credentials, password manager databases, VPN configurations, and application-specific authentication tokens, representing 33% of all disrupted malware incidents identified by eSentire.
Stolen credentials are immediately monetized via underground marketplaces that function with the speed and efficiency of legitimate e-commerce sites, enabling threat actors to filter and purchase specific organizational credentials within hours of acquisition.
Perhaps most concerning, attackers are exploiting monitoring blind spots within organizational security architectures, such as unmanaged devices, shadow IT infrastructure, and third-party supply chain partnerships.
James Maude, Field CTO at BeyondTrust, acknowledged this report shows “how identity is the new perimeter with attackers simply logging in rather than hacking in.”
The report underscores the need for phishing-resistant authentication methods such as FIDO2 and passkeys, robust third-party risk management, and adaptive access controls based on real-time risk signals.