TheWizards APT Group Utilizes SLAAC Spoofing in Sophisticated AITM Attacks
- A China-aligned APT group exploits IPv6 SLAAC to deploy malware targeting Asian individuals and organizations.
- The ultimate objective of TheWizards is to deploy WizardNet, a modular backdoor with extensive capabilities.
- The attackers rely on Spellbinder, a lateral movement tool they employ to perform AITM attacks.
Cybersecurity researchers at ESET have uncovered an advanced persistent threat (APT) campaign executed by a China-aligned hacking group, dubbed TheWizards, utilizing innovative IPv6 SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) spoofing techniques.
This group has been active since at least 2022 and has advanced capabilities enabling highly effective adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks, targeting multiple industries globally.
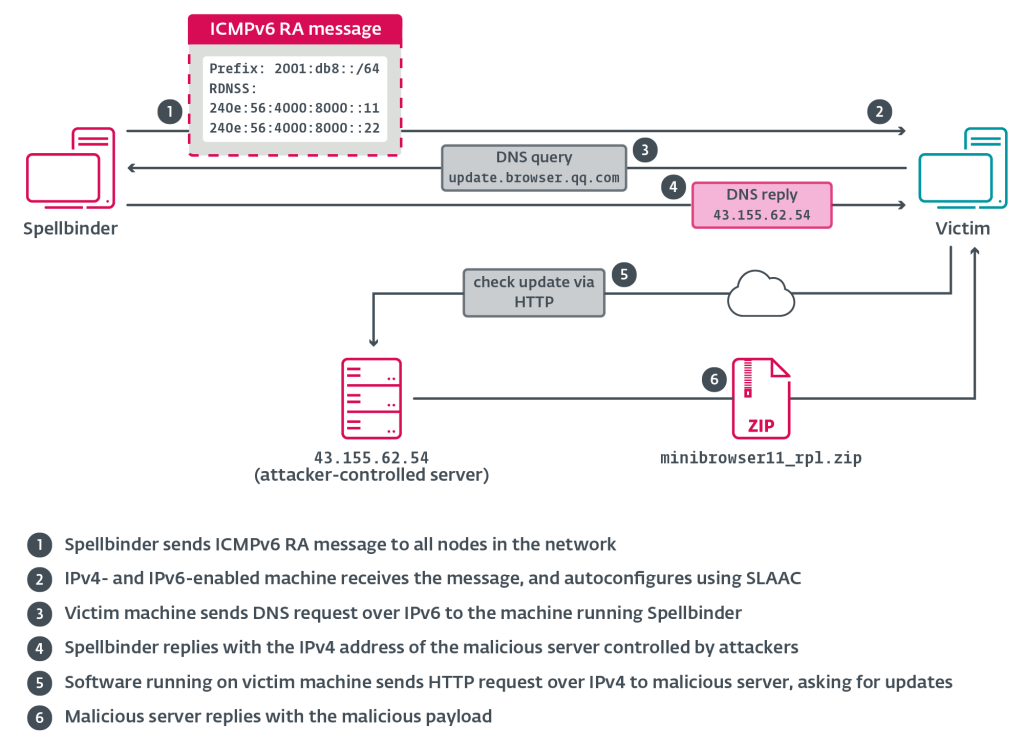
Central to TheWizards' operations is a malicious tool known as Spellbinder, which exploits vulnerabilities in network configurations to intercept and redirect traffic within compromised environments.
By leveraging SLAAC spoofing, Spellbinder enables attackers to reroute network traffic to their infrastructure, delivering malicious updates through legitimate Chinese software update mechanisms and injecting dangerous payloads.
The tool uses the network packet library WinPcap to capture and manipulate traffic. Windows machines with IPv6 and SLAAC enabled are particularly susceptible to attack.
Attackers deploy the malware to serve fake "updates" targeting software such as Tencent QQ and Sogou Pinyin. These updates embed the WizardNet backdoor, giving attackers remote control over victims' devices.
WizardNet uses advanced techniques, including registry-based persistence and memory-only execution, to evade detection. Notably, it communicates with its command-and-control (C2) servers using AES-encrypted TCP/UDP protocols, enhancing its concealment capabilities.
Spellbinder constructs malicious ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) packets, misleading victim systems into configuring compromised pathways. This allows attackers to impersonate legitimate network components.
Spellbinder answers specific DNS queries with forged addresses, redirecting traffic to attacker-controlled infrastructure. A sophisticated callback function enables Spellbinder to process, intercept, and inject malicious content into intercepted network packets.
Spellbinder has undergone iterative updates, with versions released in 2022, 2023, and 2024. These updates reflect advancements in functionality, such as capturing complex network protocols and facilitating covert data exfiltration.
The malware supports .NET module execution directly in memory, enabling versatile task handling from the C2 server. It collects system-level details, including OS architecture, installed security software, and machine-specific identifiers.
ESET researchers have identified links between TheWizards APT group and Sichuan Dianke Network Security Technology Co. (UPSEC), a Chinese company previously implicated in distributing Android malware. TheWizards’ infrastructure also exhibits similarities with UPSEC's operations, further suggesting coordinated efforts.
The identified targets include individuals and organizations in the Philippines, Cambodia, the UAE, China, and Hong Kong, making this a campaign with significant geographical reach. Key sectors affected include gambling and unidentified entities.